mirror of
https://github.com/huihut/interview.git
synced 2024-03-22 13:10:48 +08:00
README_Details 图片代码展开
This commit is contained in:
parent
159e070cf0
commit
0dac39b19d
|
|
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
#### 使用
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>const 使用</summary>
|
||||
const 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// 类
|
||||
|
|
@ -88,8 +88,6 @@ const int* function6(); // 返回一个指向常量的指针变量,使用
|
|||
int* const function7(); // 返回一个指向变量的常指针,使用:int* const p = function7();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### static
|
||||
|
||||
#### 作用
|
||||
|
|
@ -123,8 +121,7 @@ int* const function7(); // 返回一个指向变量的常指针,使用:i
|
|||
|
||||
#### 使用
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>inline 使用</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
inline 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// 声明1(加 inline,建议使用)
|
||||
|
|
@ -148,8 +145,6 @@ class A {
|
|||
inline int A::doA() { return 0; } // 需要显式内联
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 编译器对 inline 函数的处理步骤
|
||||
|
||||
1. 将 inline 函数体复制到 inline 函数调用点处;
|
||||
|
|
@ -180,8 +175,7 @@ inline int A::doA() { return 0; } // 需要显式内联
|
|||
* 内联是在编译器建议编译器内联,而虚函数的多态性在运行期,编译器无法知道运行期调用哪个代码,因此虚函数表现为多态性时(运行期)不可以内联。
|
||||
* `inline virtual` 唯一可以内联的时候是:编译器知道所调用的对象是哪个类(如 `Base::who()`),这只有在编译器具有实际对象而不是对象的指针或引用时才会发生。
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>虚函数内联使用</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
虚函数内联使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
|
|
@ -223,8 +217,6 @@ int main()
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### volatile
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
|
|
@ -240,7 +232,7 @@ volatile int i = 10;
|
|||
|
||||
断言,是宏,而非函数。assert 宏的原型定义在 `<assert.h>`(C)、`<cassert>`(C++)中,其作用是如果它的条件返回错误,则终止程序执行。可以通过定义 `NDEBUG` 来关闭 assert,但是需要在源代码的开头,`include <assert.h>` 之前。
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>assert() 使用</summary>
|
||||
assert() 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#define NDEBUG // 加上这行,则 assert 不可用
|
||||
|
|
@ -249,8 +241,6 @@ volatile int i = 10;
|
|||
assert( p != NULL ); // assert 不可用
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### sizeof()
|
||||
|
||||
* sizeof 对数组,得到整个数组所占空间大小。
|
||||
|
|
@ -260,8 +250,7 @@ assert( p != NULL ); // assert 不可用
|
|||
|
||||
设定结构体、联合以及类成员变量以 n 字节方式对齐
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>#pragma pack(n) 使用</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
#pragma pack(n) 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#pragma pack(push) // 保存对齐状态
|
||||
|
|
@ -277,8 +266,6 @@ struct test
|
|||
#pragma pack(pop) // 恢复对齐状态
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 位域
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
|
|
@ -298,7 +285,7 @@ Bit mode: 2; // mode 占 2 位
|
|||
|
||||
`extern "C"` 的作用是让 C++ 编译器将 `extern "C"` 声明的代码当作 C 语言代码处理,可以避免 C++ 因符号修饰导致代码不能和C语言库中的符号进行链接的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>extern "C" 使用</summary>
|
||||
extern "C" 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
|
|
@ -312,8 +299,6 @@ void *memset(void *, int, size_t);
|
|||
#endif
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### struct 和 typedef struct
|
||||
|
||||
#### C 中
|
||||
|
|
@ -398,7 +383,7 @@ int main() {
|
|||
* 匿名 union 不能包含 protected 成员或 private 成员
|
||||
* 全局匿名联合必须是静态(static)的
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>union 使用</summary>
|
||||
union 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#include<iostream>
|
||||
|
|
@ -434,8 +419,6 @@ int main() {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### C 实现 C++ 类
|
||||
|
||||
C 实现 C++ 的面向对象特性(封装、继承、多态)
|
||||
|
|
@ -451,7 +434,7 @@ C 实现 C++ 的面向对象特性(封装、继承、多态)
|
|||
* explicit 修饰构造函数时,可以防止隐式转换和复制初始化
|
||||
* explicit 修饰转换函数时,可以防止隐式转换,但 [按语境转换](https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/implicit_conversion) 除外
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>explicit 使用</summary>
|
||||
explicit 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
struct A
|
||||
|
|
@ -498,8 +481,6 @@ int main()
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### friend 友元类和友元函数
|
||||
|
||||
* 能访问私有成员
|
||||
|
|
@ -548,7 +529,7 @@ using namespace_name name;
|
|||
|
||||
> 一般说来,使用 using 命令比使用 using 编译命令更安全,这是由于它**只导入了指定的名称**。如果该名称与局部名称发生冲突,编译器将**发出指示**。using编译命令导入所有的名称,包括可能并不需要的名称。如果与局部名称发生冲突,则**局部名称将覆盖名称空间版本**,而编译器**并不会发出警告**。另外,名称空间的开放性意味着名称空间的名称可能分散在多个地方,这使得难以准确知道添加了哪些名称。
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>using 使用</summary>
|
||||
using 使用
|
||||
|
||||
尽量少使用 `using 指示`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -575,8 +556,6 @@ cin >> x;
|
|||
cout << x << endl;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### :: 范围解析运算符
|
||||
|
||||
#### 分类
|
||||
|
|
@ -585,7 +564,7 @@ cout << x << endl;
|
|||
2. 类作用域符(`class::name`):用于表示指定类型的作用域范围是具体某个类的
|
||||
3. 命名空间作用域符(`namespace::name`):用于表示指定类型的作用域范围是具体某个命名空间的
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>:: 使用</summary>
|
||||
:: 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
int count = 0; // 全局(::)的 count
|
||||
|
|
@ -607,8 +586,6 @@ int main() {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### enum 枚举类型
|
||||
|
||||
#### 限定作用域的枚举类型
|
||||
|
|
@ -632,7 +609,7 @@ decltype 关键字用于检查实体的声明类型或表达式的类型及值
|
|||
decltype ( expression )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>decltype 使用</summary>
|
||||
decltype 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// 尾置返回允许我们在参数列表之后声明返回类型
|
||||
|
|
@ -651,8 +628,6 @@ auto fcn2(It beg, It end) -> typename remove_reference<decltype(*beg)>::type
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 引用
|
||||
|
||||
#### 左值引用
|
||||
|
|
@ -691,7 +666,7 @@ auto fcn2(It beg, It end) -> typename remove_reference<decltype(*beg)>::type
|
|||
|
||||
用花括号初始化器列表初始化一个对象,其中对应构造函数接受一个 `std::initializer_list` 参数.
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>initializer_list 使用</summary>
|
||||
initializer_list 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
|
|
@ -744,8 +719,6 @@ int main()
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 面向对象
|
||||
|
||||
面向对象程序设计(Object-oriented programming,OOP)是种具有对象概念的程序编程典范,同时也是一种程序开发的抽象方针。
|
||||
|
|
@ -802,7 +775,7 @@ public:
|
|||
* 构造函数不能是虚函数(因为在调用构造函数时,虚表指针并没有在对象的内存空间中,必须要构造函数调用完成后才会形成虚表指针)
|
||||
* 内联函数不能是表现多态性时的虚函数,解释见:[虚函数(virtual)可以是内联函数(inline)吗?](https://github.com/huihut/interview#%E8%99%9A%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0virtual%E5%8F%AF%E4%BB%A5%E6%98%AF%E5%86%85%E8%81%94%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0inline%E5%90%97)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>动态多态使用</summary>
|
||||
动态多态使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class Shape // 形状类
|
||||
|
|
@ -840,13 +813,11 @@ int main()
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 虚析构函数
|
||||
|
||||
虚析构函数是为了解决基类的指针指向派生类对象,并用基类的指针删除派生类对象。
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>虚析构函数使用</summary>
|
||||
虚析构函数使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class Shape
|
||||
|
|
@ -872,8 +843,6 @@ int main()
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 纯虚函数
|
||||
|
||||
纯虚函数是一种特殊的虚函数,在基类中不能对虚函数给出有意义的实现,而把它声明为纯虚函数,它的实现留给该基类的派生类去做。
|
||||
|
|
@ -946,7 +915,7 @@ virtual int A() = 0;
|
|||
|
||||
用于分配、释放内存
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>malloc、free 使用</summary>
|
||||
malloc、free 使用
|
||||
|
||||
申请内存,确认是否申请成功
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -962,15 +931,13 @@ free(p);
|
|||
p = nullptr;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### new、delete
|
||||
|
||||
1. new / new[]:完成两件事,先底层调用 malloc 分配了内存,然后调用构造函数(创建对象)。
|
||||
2. delete/delete[]:也完成两件事,先调用析构函数(清理资源),然后底层调用 free 释放空间。
|
||||
3. new 在申请内存时会自动计算所需字节数,而 malloc 则需我们自己输入申请内存空间的字节数。
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>new、delete 使用</summary>
|
||||
new、delete 使用
|
||||
|
||||
申请内存,确认是否申请成功
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -983,8 +950,6 @@ int main()
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 定位 new
|
||||
|
||||
定位 new(placement new)允许我们向 new 传递额外的地址参数,从而在预先指定的内存区域创建对象。
|
||||
|
|
@ -1113,7 +1078,7 @@ unique_ptr 是 C++11 才开始提供的类型,是一种在异常时可以帮
|
|||
|
||||
* 由于强制转换为引用类型失败,dynamic_cast 运算符引发 bad_cast 异常。
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>bad_cast 使用</summary>
|
||||
bad_cast 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
try {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1124,8 +1089,6 @@ catch (bad_cast b) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 运行时类型信息 (RTTI)
|
||||
|
||||
#### dynamic_cast
|
||||
|
|
@ -1144,7 +1107,7 @@ catch (bad_cast b) {
|
|||
* type_info 类描述编译器在程序中生成的类型信息。 此类的对象可以有效存储指向类型的名称的指针。 type_info 类还可存储适合比较两个类型是否相等或比较其排列顺序的编码值。 类型的编码规则和排列顺序是未指定的,并且可能因程序而异。
|
||||
* 头文件:`typeinfo`
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>typeid、type_info 使用</summary>
|
||||
typeid、type_info 使用
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class Flyable // 能飞的
|
||||
|
|
@ -1196,8 +1159,6 @@ class doSomething(Flyable *obj) // 做些事情
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### Effective C++
|
||||
|
||||
1. 视 C++ 为一个语言联邦(C、Object-Oriented C++、Template C++、STL)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1260,14 +1221,12 @@ class doSomething(Flyable *obj) // 做些事情
|
|||
|
||||
> 英文:[Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html)
|
||||
> 中文:[C++ 风格指南](https://zh-google-styleguide.readthedocs.io/en/latest/google-cpp-styleguide/contents/)
|
||||
<details><summary>Google C++ Style Guide 图</summary>
|
||||
Google C++ Style Guide 图
|
||||
|
||||
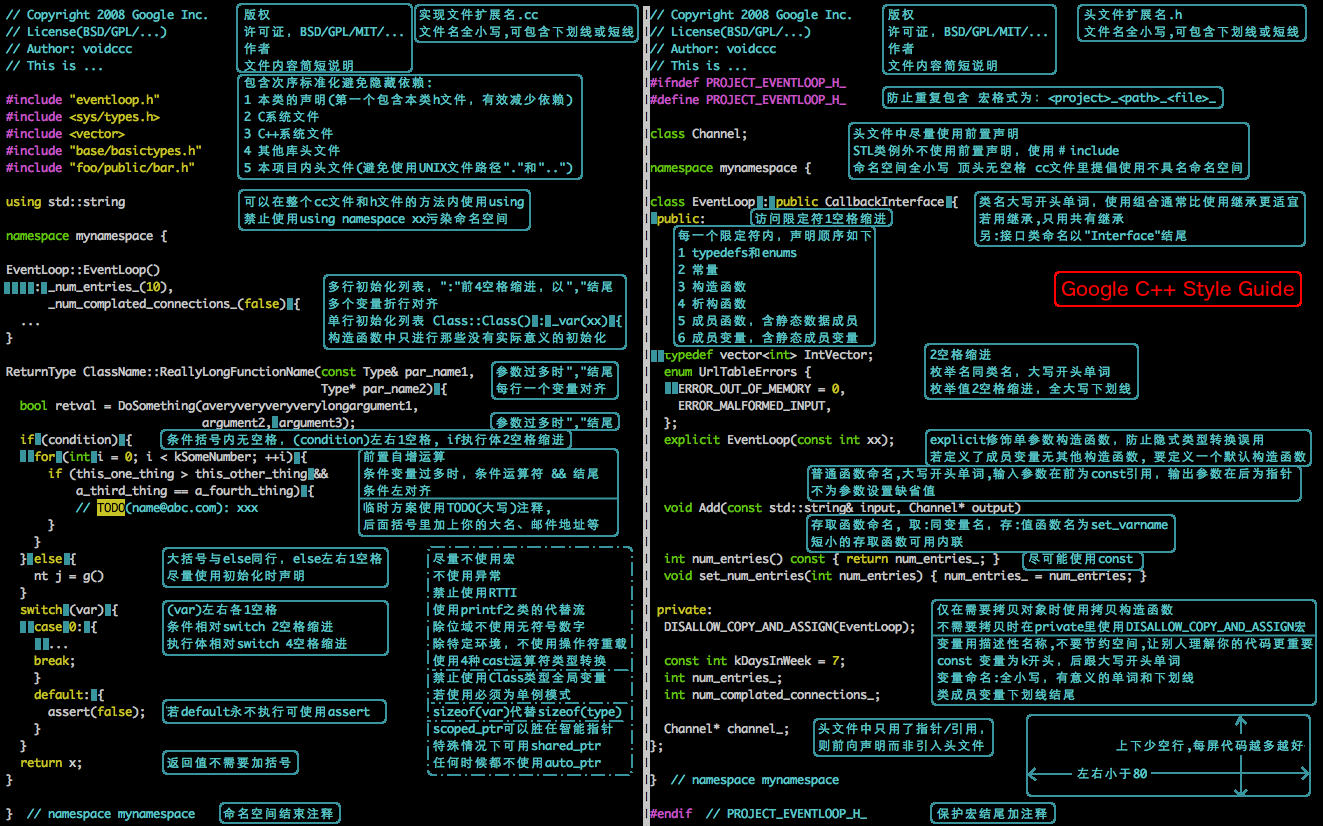
|
||||
|
||||
> 图片来源于:[CSDN . 一张图总结Google C++编程规范(Google C++ Style Guide)](https://blog.csdn.net/voidccc/article/details/37599203)
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他
|
||||
|
||||
* [Bjarne Stroustrup 的常见问题](http://www.stroustrup.com/bs_faq.html)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1314,7 +1273,7 @@ hash_multimap|哈希表|插入、删除、查找 O(1) 最差 O(n)|无序|可重
|
|||
|
||||
[SqStack.cpp](DataStructure/SqStack.cpp)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>顺序栈数据结构和图片</summary>
|
||||
顺序栈数据结构和图片
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1327,11 +1286,9 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
|
||||
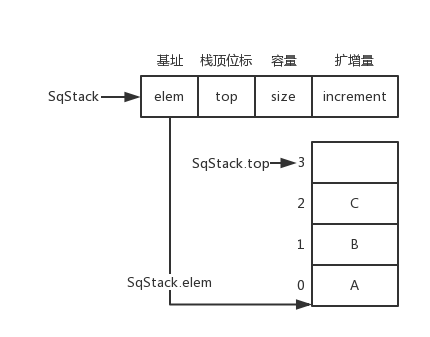
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 队列(Sequence Queue)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>队列数据结构</summary>
|
||||
队列数据结构
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1342,33 +1299,27 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
}SqQueue;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##### 非循环队列
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>非循环队列图片</summary>
|
||||
非循环队列图片
|
||||
|
||||
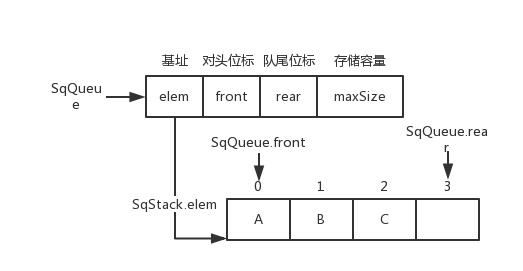
|
||||
|
||||
`SqQueue.rear++`
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##### 循环队列
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>循环队列图片</summary>
|
||||
循环队列图片
|
||||
|
||||
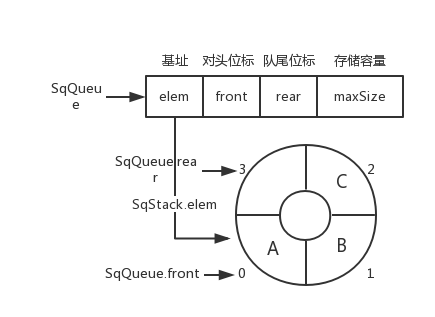
|
||||
|
||||
`SqQueue.rear = (SqQueue.rear + 1) % SqQueue.maxSize`
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 顺序表(Sequence List)
|
||||
|
||||
[SqList.cpp](DataStructure/SqList.cpp)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>顺序表数据结构和图片</summary>
|
||||
顺序表数据结构和图片
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
typedef struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1381,8 +1332,6 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
|
||||
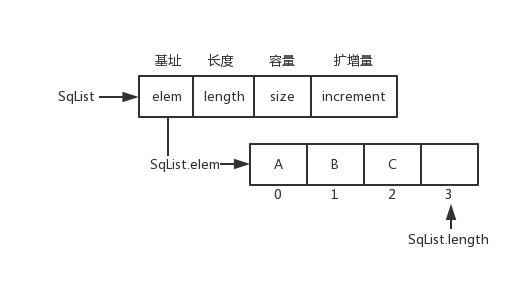
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 链式结构
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1390,7 +1339,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
|
||||
[LinkList_with_head.cpp](DataStructure/LinkList_with_head.cpp)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>链式数据结构</summary>
|
||||
链式数据结构
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
typedef struct LNode {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1399,43 +1348,32 @@ typedef struct LNode {
|
|||
} LNode, *LinkList;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 链队列(Link Queue)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>链队列图片</summary>
|
||||
链队列图片
|
||||
|
||||
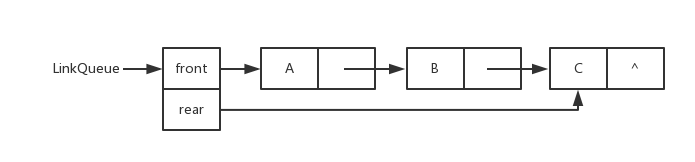
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 线性表的链式表示
|
||||
|
||||
##### 单链表(Link List)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>单链表图片</summary>
|
||||
单链表图片
|
||||
|
||||
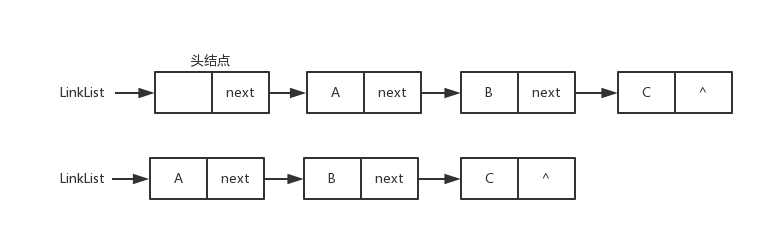
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 双向链表(Du-Link-List)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>双向链表图片</summary>
|
||||
双向链表图片
|
||||
|
||||
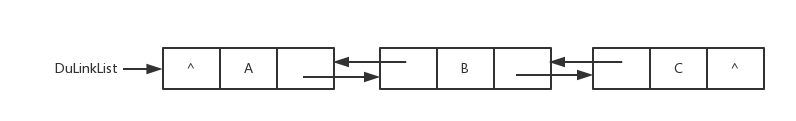
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##### 循环链表(Cir-Link-List)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>循环链表图片</summary>
|
||||
循环链表图片
|
||||
|
||||
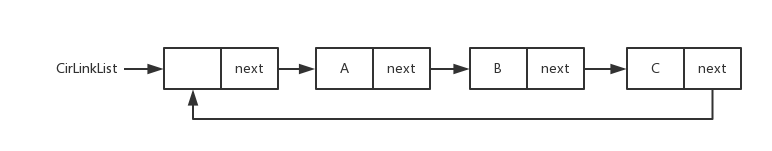
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 哈希表
|
||||
|
||||
[HashTable.cpp](DataStructure/HashTable.cpp)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1462,7 +1400,7 @@ typedef struct LNode {
|
|||
|
||||
#### 线性探测的哈希表数据结构
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>线性探测的哈希表数据结构和图片</summary>
|
||||
线性探测的哈希表数据结构和图片
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
typedef char KeyType;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1481,9 +1419,6 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
|
||||
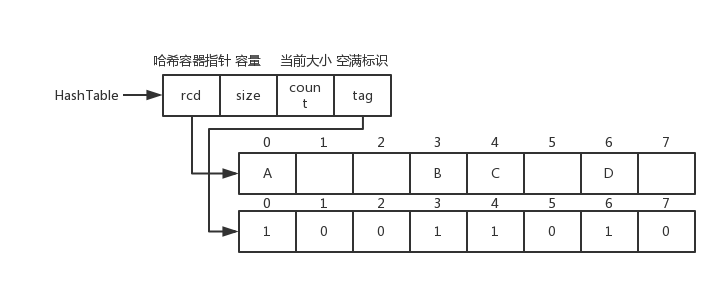
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 递归
|
||||
|
||||
#### 概念
|
||||
|
|
@ -1509,7 +1444,7 @@ typedef struct {
|
|||
|
||||
##### 头尾链表存储表示
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>广义表的头尾链表存储表示和图片</summary>
|
||||
广义表的头尾链表存储表示和图片
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// 广义表的头尾链表存储表示
|
||||
|
|
@ -1532,11 +1467,9 @@ typedef struct GLNode {
|
|||
|
||||
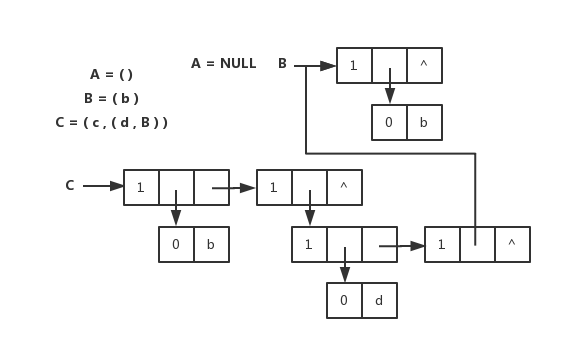
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##### 扩展线性链表存储表示
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>扩展线性链表存储表示和图片</summary>
|
||||
扩展线性链表存储表示和图片
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// 广义表的扩展线性链表存储表示
|
||||
|
|
@ -1557,8 +1490,6 @@ typedef struct GLNode1 {
|
|||
|
||||
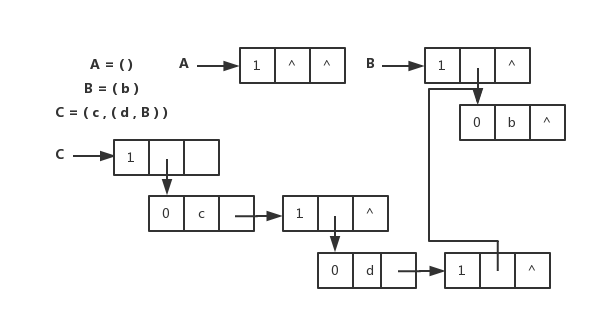
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 二叉树
|
||||
|
||||
[BinaryTree.cpp](DataStructure/BinaryTree.cpp)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1576,7 +1507,7 @@ typedef struct GLNode1 {
|
|||
|
||||
#### 存储结构
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>二叉树数据结构</summary>
|
||||
二叉树数据结构
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
typedef struct BiTNode
|
||||
|
|
@ -1586,25 +1517,18 @@ typedef struct BiTNode
|
|||
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 顺序存储
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>二叉树顺序存储图片</summary>
|
||||
二叉树顺序存储图片
|
||||
|
||||
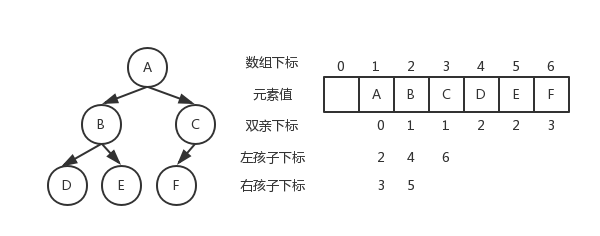
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##### 链式存储
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>二叉树链式存储图片</summary>
|
||||
二叉树链式存储图片
|
||||
|
||||
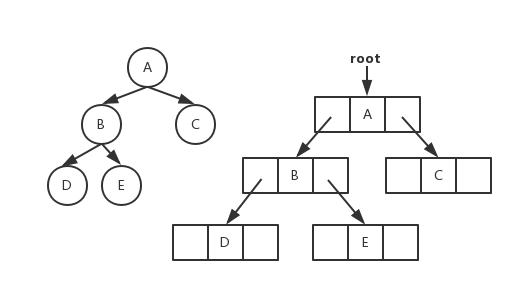
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 遍历方式
|
||||
|
||||
* 先序遍历
|
||||
|
|
@ -1646,12 +1570,10 @@ typedef struct BiTNode
|
|||
* 平衡二叉树必定是二叉搜索树,反之则不一定
|
||||
* 最小二叉平衡树的节点的公式:`F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)+1` (1 是根节点,F(n-1) 是左子树的节点数量,F(n-2) 是右子树的节点数量)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>平衡二叉树图片</summary>
|
||||
平衡二叉树图片
|
||||
|
||||
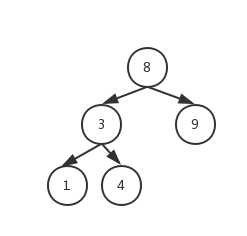
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##### 最小失衡树
|
||||
|
||||
平衡二叉树插入新结点导致失衡的子树
|
||||
|
|
@ -1692,12 +1614,10 @@ typedef struct BiTNode
|
|||
|
||||
#### B 树(B-tree)、B+ 树(B+-tree)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>B 树、B+ 树图片</summary>
|
||||
B 树、B+ 树图片
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##### 特点
|
||||
|
||||
* 一般化的二叉查找树(binary search tree)
|
||||
|
|
@ -1725,12 +1645,10 @@ typedef struct BiTNode
|
|||
|
||||
#### 八叉树
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>八叉树图片</summary>
|
||||
八叉树图片
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
八叉树(octree),或称八元树,是一种用于描述三维空间(划分空间)的树状数据结构。八叉树的每个节点表示一个正方体的体积元素,每个节点有八个子节点,这八个子节点所表示的体积元素加在一起就等于父节点的体积。一般中心点作为节点的分叉中心。
|
||||
|
||||
##### 用途
|
||||
|
|
@ -1990,17 +1908,14 @@ B树/B+树 |O(log<sub>2</sub>n) | |
|
|||
大端|12|34|56|78
|
||||
小端|78|56|34|12
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>大端小端图片</summary>
|
||||
大端小端图片
|
||||
|
||||
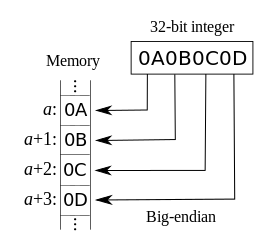
|
||||
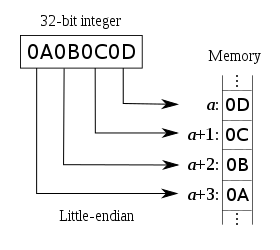
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##### 判断大端小端
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>判断大端小端</summary>
|
||||
判断大端小端
|
||||
|
||||
可以这样判断自己 CPU 字节序是大端还是小端:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2021,8 +1936,6 @@ int main()
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
##### 各架构处理器的字节序
|
||||
|
||||
* x86(Intel、AMD)、MOS Technology 6502、Z80、VAX、PDP-11 等处理器为小端序;
|
||||
|
|
@ -2284,12 +2197,10 @@ TCP 是一个基于字节流的传输服务(UDP 基于报文的),“流”
|
|||
|
||||
##### 方法
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>利用可变窗口进行流量控制</summary>
|
||||
利用可变窗口进行流量控制
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### TCP 拥塞控制
|
||||
|
||||
##### 概念
|
||||
|
|
@ -2303,14 +2214,12 @@ TCP 是一个基于字节流的传输服务(UDP 基于报文的),“流”
|
|||
* 快重传( fast retransmit )
|
||||
* 快恢复( fast recovery )
|
||||
|
||||
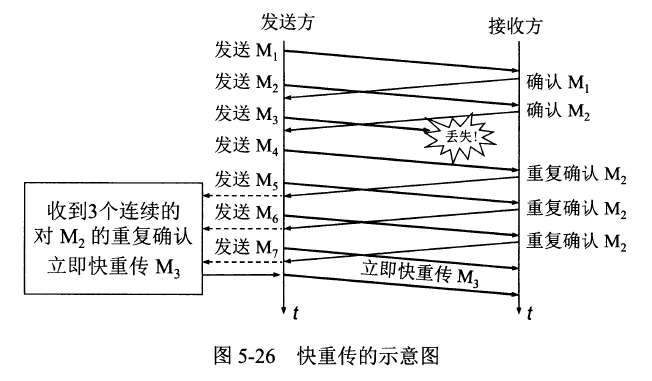
<details><summary>TCP的拥塞控制图</summary>
|
||||
TCP的拥塞控制图
|
||||
|
||||
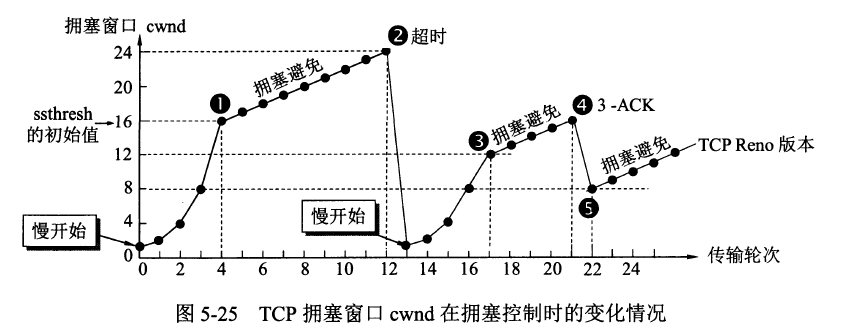
|
||||
|
||||
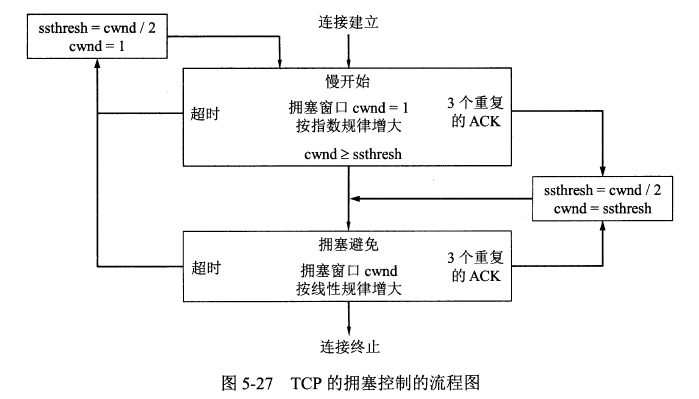
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### TCP 传输连接管理
|
||||
|
||||
> 因为 TCP 三次握手建立连接、四次挥手释放连接很重要,所以附上《计算机网络(第 7 版)-谢希仁》书中对此章的详细描述:<https://raw.githubusercontent.com/huihut/interview/master/images/TCP-transport-connection-management.png>
|
||||
|
|
@ -2373,12 +2282,10 @@ TCP 是一个基于字节流的传输服务(UDP 基于报文的),“流”
|
|||
|
||||
#### TCP 有限状态机
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>TCP 有限状态机图片</summary>
|
||||
TCP 有限状态机图片
|
||||
|
||||
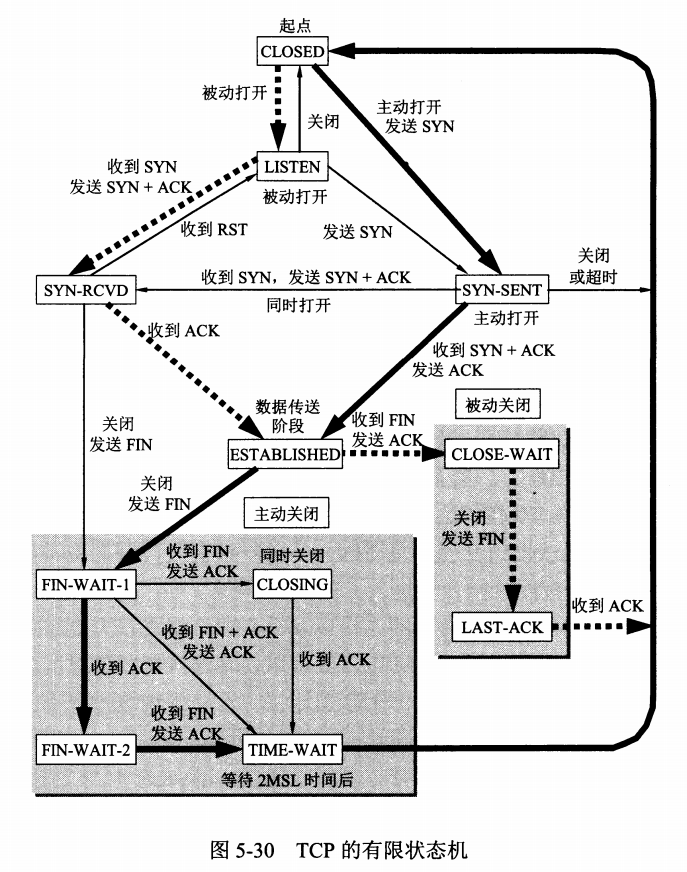
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 应用层
|
||||
|
||||
#### DNS
|
||||
|
|
@ -2825,7 +2732,7 @@ Linux 下的共享库就是普通的 ELF 共享对象。
|
|||
|
||||
#### so 共享库的编写
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>使用 CLion 编写共享库</summary>
|
||||
使用 CLion 编写共享库
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个名为 MySharedLib 的共享库
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2875,11 +2782,9 @@ void hello() {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### so 共享库的使用(被可执行项目调用)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>使用 CLion 调用共享库</summary>
|
||||
使用 CLion 调用共享库
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个名为 TestSharedLib 的可执行项目
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2933,14 +2838,12 @@ Hello, World!
|
|||
1 + 2 + 3 = 6
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### Windows 应用程序入口函数
|
||||
|
||||
* GUI(Graphical User Interface)应用,链接器选项:`/SUBSYSTEM:WINDOWS`
|
||||
* CUI(Console User Interface)应用,链接器选项:`/SUBSYSTEM:CONSOLE`
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>_tWinMain 与 _tmain 函数声明</summary>
|
||||
_tWinMain 与 _tmain 函数声明
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
Int WINAPI _tWinMain(
|
||||
|
|
@ -2955,8 +2858,6 @@ int _tmain(
|
|||
TCHAR *envp[]);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
应用程序类型|入口点函数|嵌入可执行文件的启动函数
|
||||
---|---|---
|
||||
处理ANSI字符(串)的GUI应用程序|_tWinMain(WinMain)|WinMainCRTSartup
|
||||
|
|
@ -2999,7 +2900,7 @@ int _tmain(
|
|||
|
||||
#### DLL 入口函数
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>DllMain 函数</summary>
|
||||
DllMain 函数
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
BOOL WINAPI DllMain(HINSTANCE hinstDLL, DWORD fdwReason, LPVOID lpvReserved)
|
||||
|
|
@ -3027,11 +2928,9 @@ BOOL WINAPI DllMain(HINSTANCE hinstDLL, DWORD fdwReason, LPVOID lpvReserved)
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 载入卸载库
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>LoadLibrary、LoadLibraryExA、LoadPackagedLibrary、FreeLibrary、FreeLibraryAndExitThread 函数声明</summary>
|
||||
LoadLibrary、LoadLibraryExA、LoadPackagedLibrary、FreeLibrary、FreeLibraryAndExitThread 函数声明
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// 载入库
|
||||
|
|
@ -3060,11 +2959,9 @@ VOID WINAPI FreeLibraryAndExitThread(
|
|||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 显示地链接到导出符号
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>GetProcAddress 函数声明</summary>
|
||||
GetProcAddress 函数声明
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
FARPROC GetProcAddress(
|
||||
|
|
@ -3073,8 +2970,6 @@ FARPROC GetProcAddress(
|
|||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### DumpBin.exe 查看 DLL 信息
|
||||
|
||||
在 `VS 的开发人员命令提示符` 使用 `DumpBin.exe` 可查看 DLL 库的导出段(导出的变量、函数、类名的符号)、相对虚拟地址(RVA,relative virtual address)。如:
|
||||
|
|
@ -3084,7 +2979,7 @@ DUMPBIN -exports D:\mydll.dll
|
|||
|
||||
#### LoadLibrary 与 FreeLibrary 流程图
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>LoadLibrary 与 FreeLibrary 流程图</summary>
|
||||
LoadLibrary 与 FreeLibrary 流程图
|
||||
|
||||
##### LoadLibrary
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -3094,11 +2989,9 @@ DUMPBIN -exports D:\mydll.dll
|
|||
|
||||
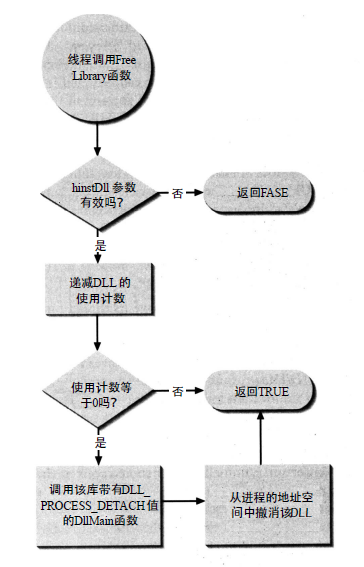
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### DLL 库的编写(导出一个 DLL 模块)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>DLL 库的编写(导出一个 DLL 模块)</summary>
|
||||
DLL 库的编写(导出一个 DLL 模块)
|
||||
DLL 头文件
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
|
|
@ -3149,11 +3042,9 @@ int Add(int nLeft, int nRight)
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
#### DLL 库的使用(运行时动态链接 DLL)
|
||||
|
||||
<details><summary>DLL 库的使用(运行时动态链接 DLL)</summary>
|
||||
DLL 库的使用(运行时动态链接 DLL)
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
// A simple program that uses LoadLibrary and
|
||||
|
|
@ -3200,8 +3091,6 @@ int main( void )
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### 运行库(Runtime Library)
|
||||
|
||||
#### 典型程序运行步骤
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user