diff --git a/README_Details.md b/README_Details.md
index 1cc71d7..1b84a4c 100644
--- a/README_Details.md
+++ b/README_Details.md
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@
#### 使用
-const 使用
+const 使用
```cpp
// 类
@@ -88,8 +88,6 @@ const int* function6(); // 返回一个指向常量的指针变量,使用
int* const function7(); // 返回一个指向变量的常指针,使用:int* const p = function7();
```
-inline 使用
-
+inline 使用
```cpp
// 声明1(加 inline,建议使用)
@@ -148,8 +145,6 @@ class A {
inline int A::doA() { return 0; } // 需要显式内联
```
-虚函数内联使用
-
+虚函数内联使用
```cpp
#include
@@ -223,8 +217,6 @@ int main()
}
```
-assert() 使用
+assert() 使用
```cpp
#define NDEBUG // 加上这行,则 assert 不可用
@@ -249,8 +241,6 @@ volatile int i = 10;
assert( p != NULL ); // assert 不可用
```
-#pragma pack(n) 使用
-
+#pragma pack(n) 使用
```cpp
#pragma pack(push) // 保存对齐状态
@@ -277,8 +266,6 @@ struct test
#pragma pack(pop) // 恢复对齐状态
```
-extern "C" 使用
+extern "C" 使用
```cpp
#ifdef __cplusplus
@@ -312,8 +299,6 @@ void *memset(void *, int, size_t);
#endif
```
-union 使用
+union 使用
```cpp
#include
@@ -434,8 +419,6 @@ int main() {
}
```
-explicit 使用
+explicit 使用
```cpp
struct A
@@ -498,8 +481,6 @@ int main()
}
```
-using 使用
+using 使用
尽量少使用 `using 指示`
@@ -575,8 +556,6 @@ cin >> x;
cout << x << endl;
```
-:: 使用
+:: 使用
```cpp
int count = 0; // 全局(::)的 count
@@ -607,8 +586,6 @@ int main() {
}
```
-decltype 使用
+decltype 使用
```cpp
// 尾置返回允许我们在参数列表之后声明返回类型
@@ -651,8 +628,6 @@ auto fcn2(It beg, It end) -> typename remove_reference::type
}
```
-initializer_list 使用
+initializer_list 使用
```cpp
#include
@@ -744,8 +719,6 @@ int main()
}
```
-动态多态使用
+动态多态使用
```cpp
class Shape // 形状类
@@ -840,13 +813,11 @@ int main()
}
```
-虚析构函数使用
+虚析构函数使用
```cpp
class Shape
@@ -872,8 +843,6 @@ int main()
}
```
-malloc、free 使用
+malloc、free 使用
申请内存,确认是否申请成功
@@ -962,15 +931,13 @@ free(p);
p = nullptr;
```
-new、delete 使用
+new、delete 使用
申请内存,确认是否申请成功
@@ -983,8 +950,6 @@ int main()
}
```
-bad_cast 使用
+bad_cast 使用
```cpp
try {
@@ -1124,8 +1089,6 @@ catch (bad_cast b) {
}
```
-typeid、type_info 使用
+typeid、type_info 使用
```cpp
class Flyable // 能飞的
@@ -1196,8 +1159,6 @@ class doSomething(Flyable *obj) // 做些事情
};
```
-Google C++ Style Guide 图
+Google C++ Style Guide 图
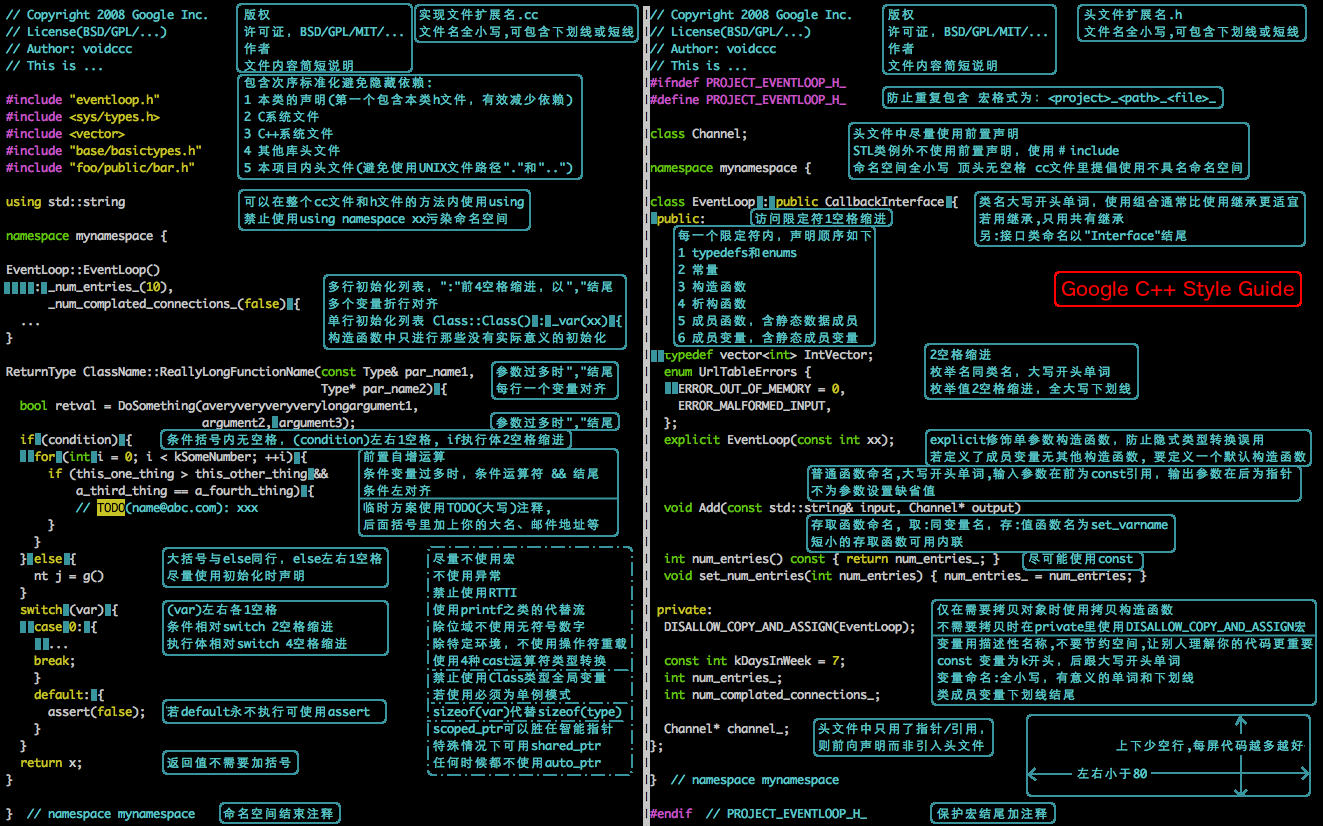
> 图片来源于:[CSDN . 一张图总结Google C++编程规范(Google C++ Style Guide)](https://blog.csdn.net/voidccc/article/details/37599203)
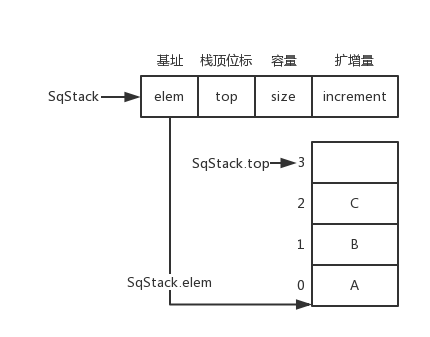
-顺序栈数据结构和图片
+顺序栈数据结构和图片
```cpp
typedef struct {
@@ -1327,11 +1286,9 @@ typedef struct {
-队列数据结构
+队列数据结构
```cpp
typedef struct {
@@ -1342,33 +1299,27 @@ typedef struct {
}SqQueue;
```
-非循环队列图片
+非循环队列图片
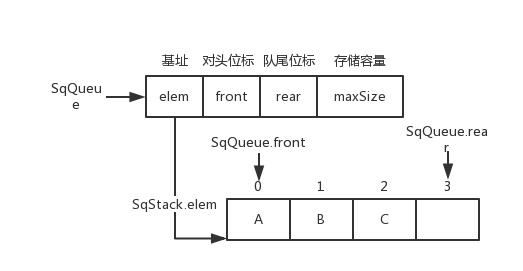
`SqQueue.rear++`
-循环队列图片
+循环队列图片
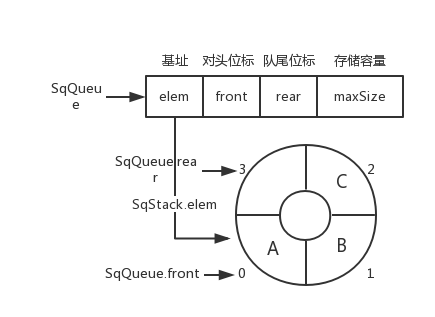
`SqQueue.rear = (SqQueue.rear + 1) % SqQueue.maxSize`
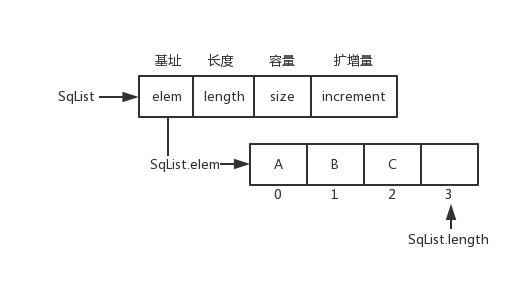
-顺序表数据结构和图片
+顺序表数据结构和图片
```cpp
typedef struct {
@@ -1381,8 +1332,6 @@ typedef struct {
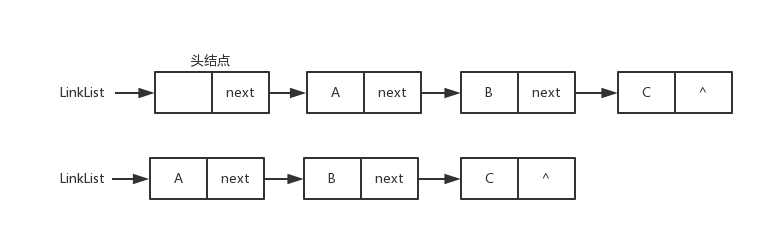
-链式数据结构
+链式数据结构
```cpp
typedef struct LNode {
@@ -1399,43 +1348,32 @@ typedef struct LNode {
} LNode, *LinkList;
```
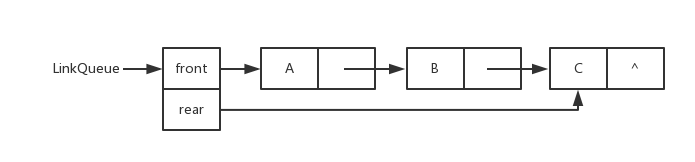
-链队列图片
+链队列图片
-单链表图片
+单链表图片
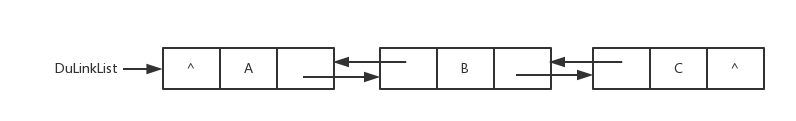
-双向链表图片
+双向链表图片
-循环链表图片
+循环链表图片
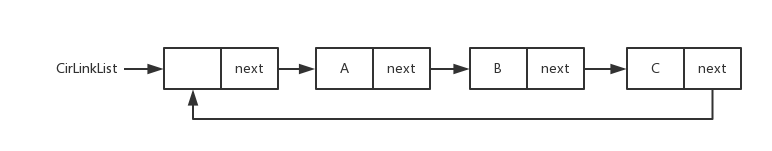
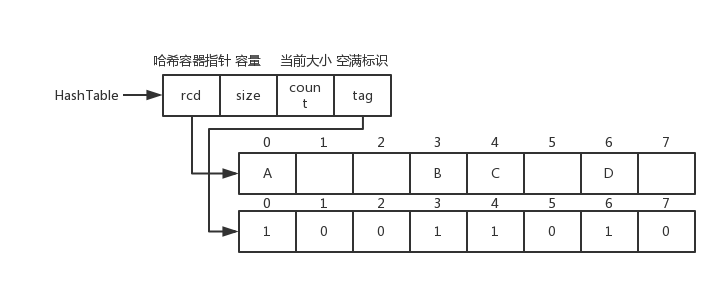
-线性探测的哈希表数据结构和图片
+线性探测的哈希表数据结构和图片
```cpp
typedef char KeyType;
@@ -1481,9 +1419,6 @@ typedef struct {
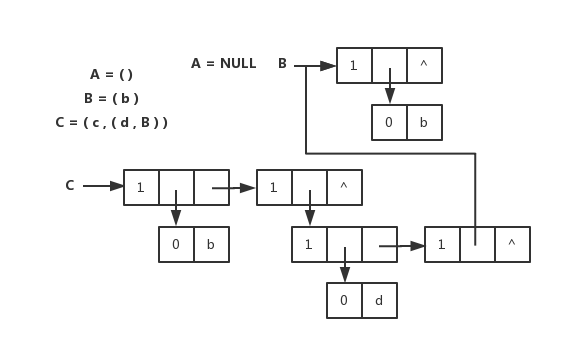
-广义表的头尾链表存储表示和图片
+广义表的头尾链表存储表示和图片
```cpp
// 广义表的头尾链表存储表示
@@ -1532,11 +1467,9 @@ typedef struct GLNode {
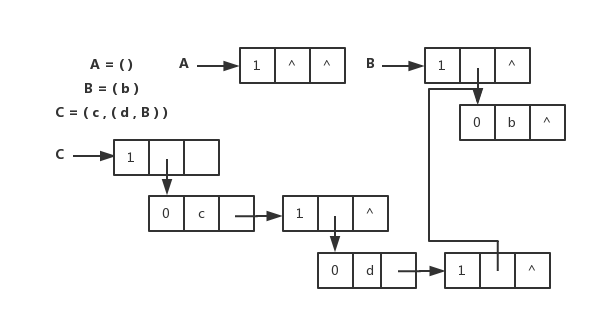
-扩展线性链表存储表示和图片
+扩展线性链表存储表示和图片
```cpp
// 广义表的扩展线性链表存储表示
@@ -1557,8 +1490,6 @@ typedef struct GLNode1 {
-二叉树数据结构
+二叉树数据结构
```cpp
typedef struct BiTNode
@@ -1586,25 +1517,18 @@ typedef struct BiTNode
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
```
-二叉树顺序存储图片
+二叉树顺序存储图片
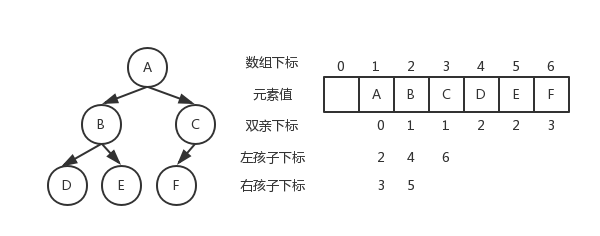
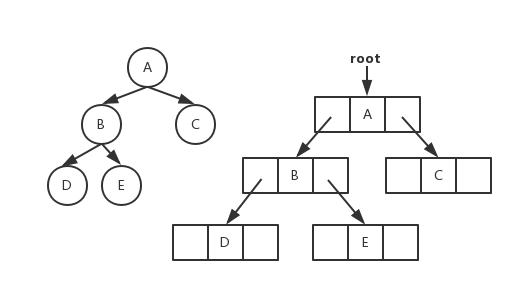
-二叉树链式存储图片
+二叉树链式存储图片
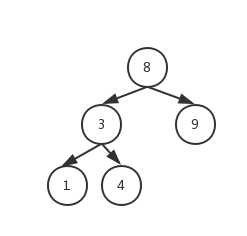
-平衡二叉树图片
+平衡二叉树图片
-B 树、B+ 树图片
+B 树、B+ 树图片

-八叉树图片
+八叉树图片

-大端小端图片
+大端小端图片
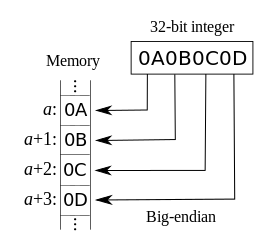
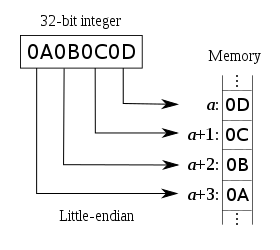
-判断大端小端
+判断大端小端
可以这样判断自己 CPU 字节序是大端还是小端:
@@ -2021,8 +1936,6 @@ int main()
}
```
-利用可变窗口进行流量控制
+利用可变窗口进行流量控制

-TCP的拥塞控制图
+TCP的拥塞控制图
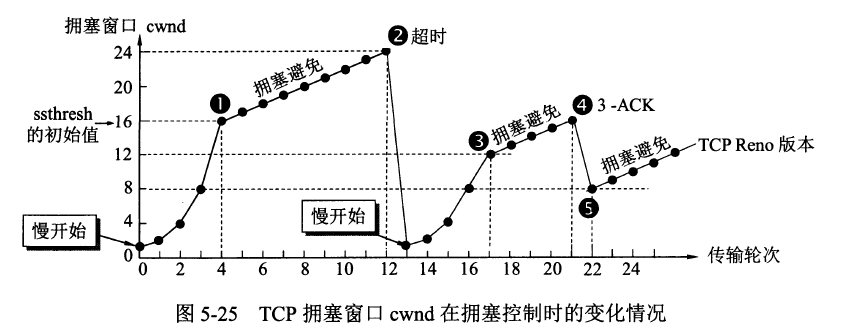
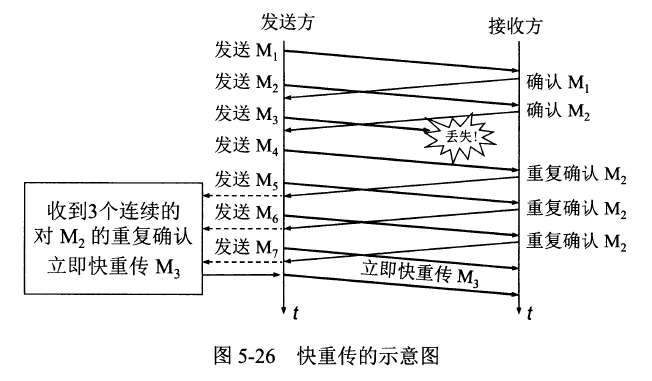
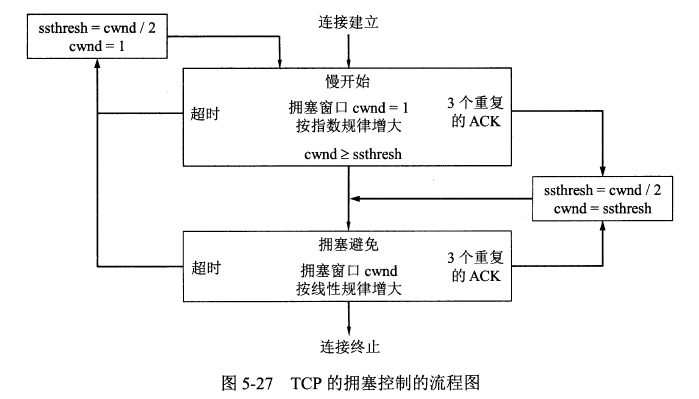
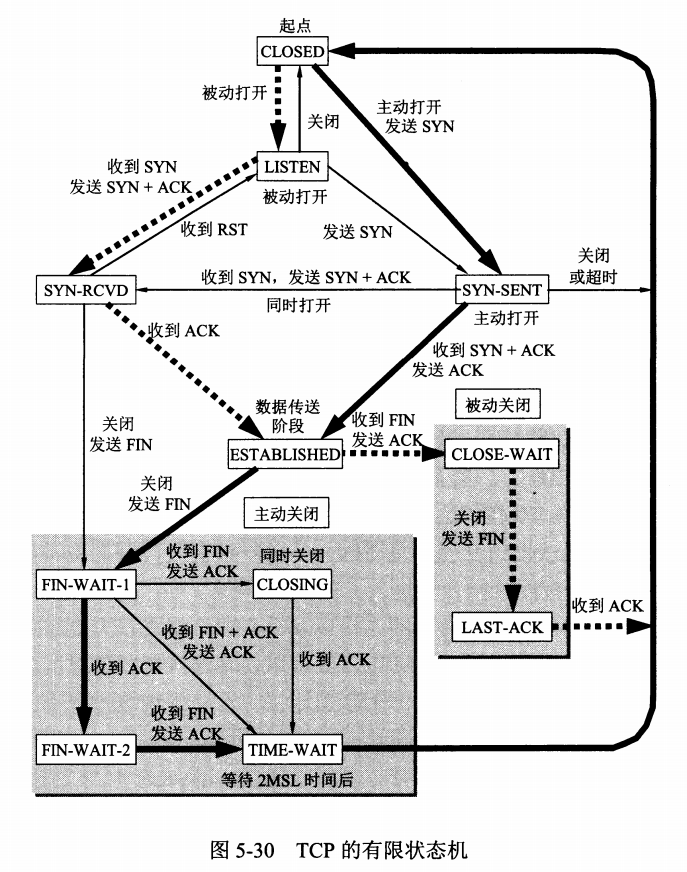
-TCP 有限状态机图片
+TCP 有限状态机图片
-使用 CLion 编写共享库
+使用 CLion 编写共享库
创建一个名为 MySharedLib 的共享库
@@ -2875,11 +2782,9 @@ void hello() {
}
```
-使用 CLion 调用共享库
+使用 CLion 调用共享库
创建一个名为 TestSharedLib 的可执行项目
@@ -2933,14 +2838,12 @@ Hello, World!
1 + 2 + 3 = 6
```
-_tWinMain 与 _tmain 函数声明
+_tWinMain 与 _tmain 函数声明
```cpp
Int WINAPI _tWinMain(
@@ -2955,8 +2858,6 @@ int _tmain(
TCHAR *envp[]);
```
-DllMain 函数
+DllMain 函数
```cpp
BOOL WINAPI DllMain(HINSTANCE hinstDLL, DWORD fdwReason, LPVOID lpvReserved)
@@ -3027,11 +2928,9 @@ BOOL WINAPI DllMain(HINSTANCE hinstDLL, DWORD fdwReason, LPVOID lpvReserved)
}
```
-LoadLibrary、LoadLibraryExA、LoadPackagedLibrary、FreeLibrary、FreeLibraryAndExitThread 函数声明
+LoadLibrary、LoadLibraryExA、LoadPackagedLibrary、FreeLibrary、FreeLibraryAndExitThread 函数声明
```cpp
// 载入库
@@ -3060,11 +2959,9 @@ VOID WINAPI FreeLibraryAndExitThread(
);
```
-GetProcAddress 函数声明
+GetProcAddress 函数声明
```cpp
FARPROC GetProcAddress(
@@ -3073,8 +2970,6 @@ FARPROC GetProcAddress(
);
```
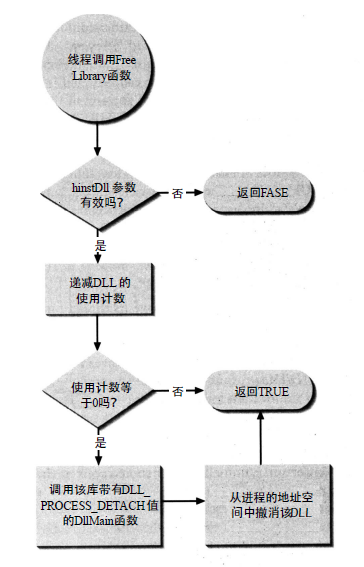
-LoadLibrary 与 FreeLibrary 流程图
+LoadLibrary 与 FreeLibrary 流程图
##### LoadLibrary
@@ -3094,11 +2989,9 @@ DUMPBIN -exports D:\mydll.dll
-DLL 库的编写(导出一个 DLL 模块)
+DLL 库的编写(导出一个 DLL 模块)
DLL 头文件
```cpp
@@ -3149,11 +3042,9 @@ int Add(int nLeft, int nRight)
}
```
-DLL 库的使用(运行时动态链接 DLL)
+DLL 库的使用(运行时动态链接 DLL)
```cpp
// A simple program that uses LoadLibrary and
@@ -3200,8 +3091,6 @@ int main( void )
}
```
-