15 KiB
一、I/O 模型
一个输入操作通常包括两个阶段:
- 等待数据准备好
- 从内核向进程复制数据
对于一个套接字上的输入操作,第一步通常涉及等待数据从网络中到达。当所等待分组到达时,它被复制到内核中的某个缓冲区。第二步就是把数据从内核缓冲区复制到应用进程缓冲区。
Unix 下有五种 I/O 模型:
- 阻塞式 I/O
- 非阻塞式 I/O
- I/O 复用(select 和 poll)
- 信号驱动式 I/O(SIGIO)
- 异步 I/O(AIO)
阻塞式 I/O
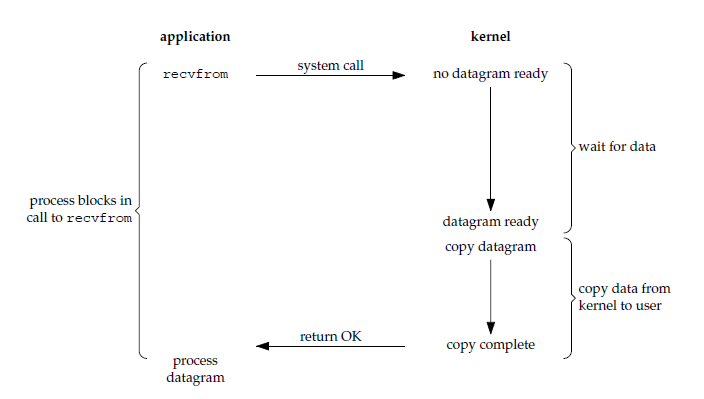
应用进程被阻塞,直到数据复制到应用进程缓冲区中才返回。
应该注意到,在阻塞的过程中,其它程序还可以执行,因此阻塞不意味着整个操作系统都被阻塞。因为其他程序还可以执行,因此不消耗 CPU 时间,这种模型的执行效率会比较高。
下图中,recvfrom 用于接收 Socket 传来的数据,并复制到应用进程的缓冲区 buf 中。这里把 recvfrom() 当成系统调用。
ssize_t recvfrom(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len, int flags, struct sockaddr *src_addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
非阻塞式 I/O
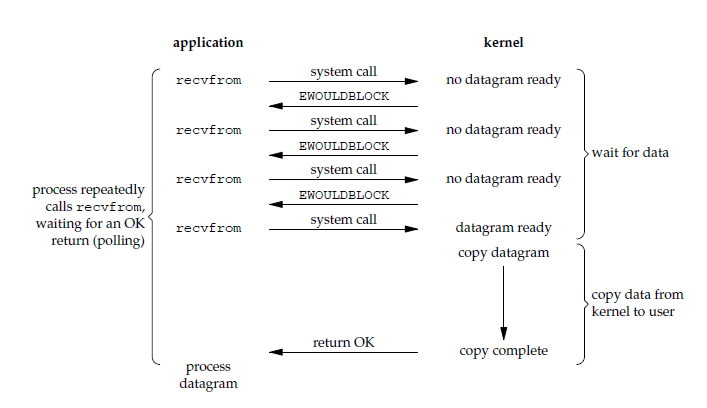
应用进程执行系统调用之后,内核返回一个错误码。应用进程可以继续执行,但是需要不断的执行系统调用来获知 I/O 是否完成,这种方式称为轮询(polling)。
由于 CPU 要处理更多的系统调用,因此这种模型是比较低效的。
I/O 复用
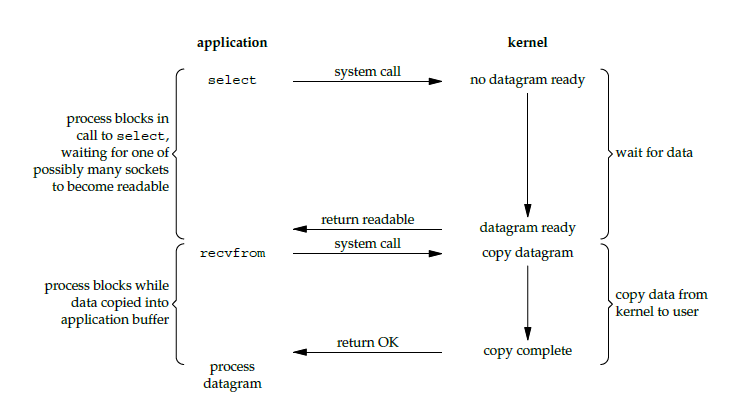
使用 select 或者 poll 等待数据,并且可以等待多个套接字中的任何一个变为可读,这一过程会被阻塞,当某一个套接字可读时返回。之后再使用 recvfrom 把数据从内核复制到进程中。
它可以让单个进程具有处理多个 I/O 事件的能力。又被称为 Event Driven I/O,即事件驱动 I/O。
如果一个 Web 服务器没有 I/O 复用,那么每一个 Socket 连接都需要创建一个线程去处理。如果同时有几万个连接,那么就需要创建相同数量的线程。并且相比于多进程和多线程技术,I/O 复用不需要进程线程创建和切换的开销,系统开销更小。
信号驱动 I/O
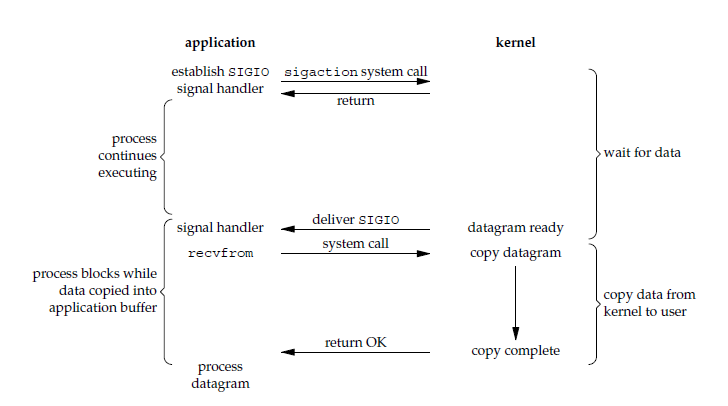
应用进程使用 sigaction 系统调用,内核立即返回,应用进程可以继续执行,也就是说等待数据阶段应用进程是非阻塞的。内核在数据到达时向应用进程发送 SIGIO 信号,应用进程收到之后在信号处理程序中调用 recvfrom 将数据从内核复制到应用进程中。
相比于非阻塞式 I/O 的轮询方式,信号驱动 I/O 的 CPU 利用率更高。
异步 I/O
进行 aio_read 系统调用会立即返回,应用进程继续执行,不会被阻塞,内核会在所有操作完成之后向应用进程发送信号。
异步 I/O 与信号驱动 I/O 的区别在于,异步 I/O 的信号是通知应用进程 I/O 完成,而信号驱动 I/O 的信号是通知应用进程可以开始 I/O。

同步 I/O 与异步 I/O
- 同步 I/O:应用进程在调用 recvfrom 操作时会阻塞。
- 异步 I/O:不会阻塞。
阻塞式 I/O、非阻塞式 I/O、I/O 复用和信号驱动 I/O 都是同步 I/O,虽然非阻塞式 I/O 和信号驱动 I/O 在等待数据阶段不会阻塞,但是在之后的将数据从内核复制到应用进程这个操作会阻塞。
五大 I/O 模型比较
前四种 I/O 模型的主要区别在于第一个阶段,而第二个阶段是一样的:将数据从内核复制到应用进程过程中,应用进程会被阻塞。
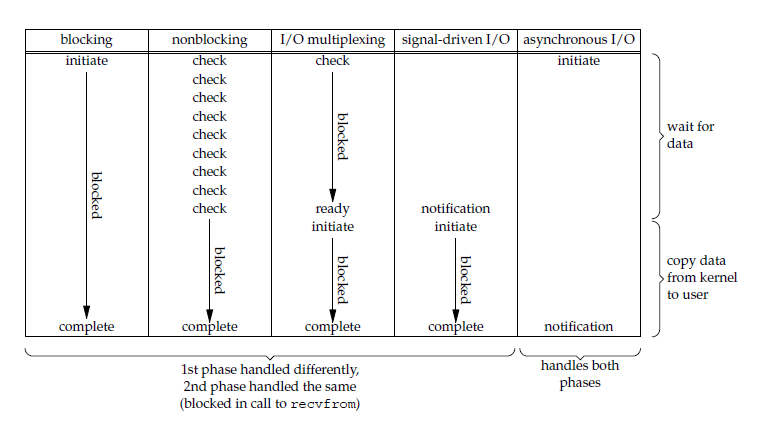
二、I/O 复用
select/poll/epoll 都是 I/O 多路复用的具体实现,select 出现的最早,之后是 poll,再是 epoll。
select
int select(int n, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
readset, writeset, exceptset 参数,分别对应读、写、异常条件的描述符集合。
timeout 参数告知内核等待所指定描述符中的任何一个就绪的最长时间;
成功调用返回结果大于 0;出错返回结果为 -1;超时返回结果为 0。
每次调用 select 都需要将 readfds, writefds, exceptfds 链表内容全部从应用进程缓冲区复制到内核缓冲区。
返回结果中内核并没有声明 fd_set 中哪些描述符已经准备好,所以如果返回值大于 0 时,应用进程需要遍历所有的 fd_set。
select 最多支持 1024 个描述符,其中 1024 由内核的 FD_SETSIZE 决定。如果需要打破该限制可以修改 FD_SETSIZE,然后重新编译内核。
fd_set fd_in, fd_out;
struct timeval tv;
// Reset the sets
FD_ZERO( &fd_in );
FD_ZERO( &fd_out );
// Monitor sock1 for input events
FD_SET( sock1, &fd_in );
// Monitor sock2 for output events
FD_SET( sock2, &fd_out );
// Find out which socket has the largest numeric value as select requires it
int largest_sock = sock1 > sock2 ? sock1 : sock2;
// Wait up to 10 seconds
tv.tv_sec = 10;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
// Call the select
int ret = select( largest_sock + 1, &fd_in, &fd_out, NULL, &tv );
// Check if select actually succeed
if ( ret == -1 )
// report error and abort
else if ( ret == 0 )
// timeout; no event detected
else
{
if ( FD_ISSET( sock1, &fd_in ) )
// input event on sock1
if ( FD_ISSET( sock2, &fd_out ) )
// output event on sock2
}
poll
int poll(struct pollfd *fds, unsigned int nfds, int timeout);
struct pollfd {
int fd; // 文件描述符
short events; // 监视的请求事件
short revents; // 已发生的事件
};
它和 select 功能基本相同,同样需要每次都将描述符从应用进程缓冲区复制到内核缓冲区,调用返回后同样需要进行轮询才能知道哪些描述符已经准备好。
poll 取消了 1024 个描述符数量上限,但是数量太大以后不能保证执行效率,因为复制大量内存到内核十分低效,所需时间与描述符数量成正比。
poll 在描述符的重复利用上比 select 的 fd_set 会更好。
如果在多线程下,如果一个线程对某个描述符调用了 poll 系统调用,但是另一个线程关闭了该描述符,会导致 poll 调用结果不确定,该问题同样出现在 select 中。
// The structure for two events
struct pollfd fds[2];
// Monitor sock1 for input
fds[0].fd = sock1;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
// Monitor sock2 for output
fds[1].fd = sock2;
fds[1].events = POLLOUT;
// Wait 10 seconds
int ret = poll( &fds, 2, 10000 );
// Check if poll actually succeed
if ( ret == -1 )
// report error and abort
else if ( ret == 0 )
// timeout; no event detected
else
{
// If we detect the event, zero it out so we can reuse the structure
if ( pfd[0].revents & POLLIN )
pfd[0].revents = 0;
// input event on sock1
if ( pfd[1].revents & POLLOUT )
pfd[1].revents = 0;
// output event on sock2
}
epoll
int epoll_create(int size);
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event * events, int maxevents, int timeout);
epoll 仅适用于 Linux OS。
它是 select 和 poll 的增强版,更加灵活而且没有描述符数量限制。
它将用户关心的描述符放到内核的一个事件表中,从而只需要在用户进程缓冲区和内核缓冲区拷贝一次。
select 和 poll 方式中,进程只有在调用一定的方法后,内核才对所有监视的描述符进行扫描。而 epoll 事先通过 epoll_ctl() 来注册描述符,一旦基于某个描述符就绪时,内核会采用类似 callback 的回调机制,迅速激活这个描述符,当进程调用 epoll_wait() 时便得到通知。
新版本的 epoll_create(int size) 参数 size 不起任何作用,在旧版本的 epoll 中如果描述符的数量大于 size,不保证服务质量。
epoll_ctl() 执行一次系统调用,用于向内核注册新的描述符或者是改变某个文件描述符的状态。已注册的描述符在内核中会被维护在一棵红黑树上,通过回调函数内核会将 I/O 准备好的描述符加入到一个链表中管理。
epoll_wait() 取出在内核中通过链表维护的 I/O 准备好的描述符,将他们从内核复制到应用进程中,不需要像 select/poll 对注册的所有描述符遍历一遍。
epoll 对多线程编程更有友好,同时多个线程对同一个描述符调用了 epoll_wait() 也不会产生像 select/poll 的不确定情况。或者一个线程调用了 epoll_wait() 另一个线程关闭了同一个描述符也不会产生不确定情况。
// Create the epoll descriptor. Only one is needed per app, and is used to monitor all sockets.
// The function argument is ignored (it was not before, but now it is), so put your favorite number here
int pollingfd = epoll_create( 0xCAFE );
if ( pollingfd < 0 )
// report error
// Initialize the epoll structure in case more members are added in future
struct epoll_event ev = { 0 };
// Associate the connection class instance with the event. You can associate anything
// you want, epoll does not use this information. We store a connection class pointer, pConnection1
ev.data.ptr = pConnection1;
// Monitor for input, and do not automatically rearm the descriptor after the event
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLONESHOT;
// Add the descriptor into the monitoring list. We can do it even if another thread is
// waiting in epoll_wait - the descriptor will be properly added
if ( epoll_ctl( epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, pConnection1->getSocket(), &ev ) != 0 )
// report error
// Wait for up to 20 events (assuming we have added maybe 200 sockets before that it may happen)
struct epoll_event pevents[ 20 ];
// Wait for 10 seconds, and retrieve less than 20 epoll_event and store them into epoll_event array
int ready = epoll_wait( pollingfd, pevents, 20, 10000 );
// Check if epoll actually succeed
if ( ret == -1 )
// report error and abort
else if ( ret == 0 )
// timeout; no event detected
else
{
// Check if any events detected
for ( int i = 0; i < ret; i++ )
{
if ( pevents[i].events & EPOLLIN )
{
// Get back our connection pointer
Connection * c = (Connection*) pevents[i].data.ptr;
c->handleReadEvent();
}
}
}
select 和 poll 比较
1. 功能
它们提供了几乎相同的功能,但是在一些细节上有所不同:
- select 会修改 fd_set 参数,而 poll 不会;
- select 默认只能监听 1024 个描述符,如果要监听更多的话,需要修改 FD_SETSIZE 之后重新编译;
- poll 提供了更多的事件类型。
2. 速度
poll 和 select 在速度上都很慢。
- 它们都采取轮询的方式来找到 I/O 完成的描述符,如果描述符很多,那么速度就会很慢;
- select 只使用每个描述符的 3 位,而 poll 通常需要使用 64 位,因此 poll 需要在用户进程和内核之间复制更多的数据。
3. 可移植性
几乎所有的系统都支持 select,但是只有比较新的系统支持 poll。
epoll 工作模式
epoll_event 有两种触发模式:LT(level trigger)和 ET(edge trigger)。
1. LT 模式
当 epoll_wait() 检测到描述符事件发生并将此事件通知应用程序,应用程序可以不立即处理该事件。下次调用 epoll_wait() 时,会再次响应应用程序并通知此事件。是默认的一种模式,并且同时支持 Blocking 和 No-Blocking。
2. ET 模式
当 epoll_wait() 检测到描述符事件发生并将此事件通知应用程序,应用程序必须立即处理该事件。如果不处理,下次调用 epoll_wait() 时,不会再次响应应用程序并通知此事件。很大程度上减少了 epoll 事件被重复触发的次数,因此效率要比 LT 模式高。只支持 No-Blocking,以避免由于一个文件句柄的阻塞读/阻塞写操作把处理多个文件描述符的任务饿死。
应用场景
很容易产生一种错觉认为只要用 epoll 就可以了,select poll 都是历史遗留问题,并没有什么应用场景,其实并不是这样的。
1. select 应用场景
select() poll() epoll_wait() 都有一个 timeout 参数,在 select() 中 timeout 的精确度为 1ns,而 poll() 和 epoll_wait() 中则为 1ms。所以 select 更加适用于实时要求更高的场景,比如核反应堆的控制。
select 历史更加悠久,它的可移植性更好,几乎被所有主流平台所支持。
2. poll 应用场景
poll 没有最大描述符数量的限制,如果平台支持应该采用 poll 且对实时性要求并不是十分严格,而不是 select。
需要同时监控小于 1000 个描述符。没有必要使用 epoll,因为这个应用场景下并不能体现 epoll 的优势。
需要监控的描述符状态变化多,而且都是非常短暂的。因为 epoll 中的所有描述符都存储在内核中,造成每次需要对描述符的状态改变都需要通过 epoll_ctl() 进行系统调用,频繁系统调用降低效率。并且epoll 的描述符存储在内核,不容易调试。
3. epoll 应用场景
程序只需要运行在 Linux 平台上,有非常大量的描述符需要同时轮询,而且这些连接最好是长连接。
4. 性能对比
参考资料
- Stevens W R, Fenner B, Rudoff A M. UNIX network programming[M]. Addison-Wesley Professional, 2004.
- Boost application performance using asynchronous I/O
- Synchronous and Asynchronous I/O
- Linux IO 模式及 select、poll、epoll 详解
- poll vs select vs event-based