4.6 KiB
4.6 KiB
汉诺塔

有三个柱子,分别为 from、buffer、to。需要将 from 上的圆盘全部移动到 to 上,并且要保证小圆盘始终在大圆盘上。
这是一个经典的递归问题,分为三步求解:
① 将 n-1 个圆盘从 from -> buffer

② 将 1 个圆盘从 from -> to
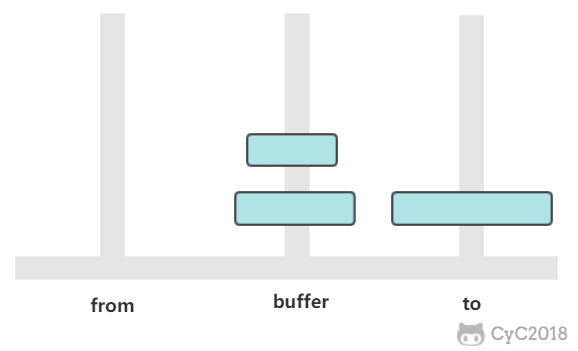
③ 将 n-1 个圆盘从 buffer -> to

如果只有一个圆盘,那么只需要进行一次移动操作。
从上面的讨论可以知道,an = 2 * an-1 + 1,显然 an = 2n - 1,n 个圆盘需要移动 2n - 1 次。
public class Hanoi {
public static void move(int n, String from, String buffer, String to) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("from " + from + " to " + to);
return;
}
move(n - 1, from, to, buffer);
move(1, from, buffer, to);
move(n - 1, buffer, from, to);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hanoi.move(3, "H1", "H2", "H3");
}
}
from H1 to H3
from H1 to H2
from H3 to H2
from H1 to H3
from H2 to H1
from H2 to H3
from H1 to H3
哈夫曼编码
根据数据出现的频率对数据进行编码,从而压缩原始数据。
例如对于一个文本文件,其中各种字符出现的次数如下:
- a : 10
- b : 20
- c : 40
- d : 80
可以将每种字符转换成二进制编码,例如将 a 转换为 00,b 转换为 01,c 转换为 10,d 转换为 11。这是最简单的一种编码方式,没有考虑各个字符的权值(出现频率)。而哈夫曼编码采用了贪心策略,使出现频率最高的字符的编码最短,从而保证整体的编码长度最短。
首先生成一颗哈夫曼树,每次生成过程中选取频率最少的两个节点,生成一个新节点作为它们的父节点,并且新节点的频率为两个节点的和。选取频率最少的原因是,生成过程使得先选取的节点位于树的更低层,那么需要的编码长度更长,频率更少可以使得总编码长度更少。
生成编码时,从根节点出发,向左遍历则添加二进制位 0,向右则添加二进制位 1,直到遍历到叶子节点,叶子节点代表的字符的编码就是这个路径编码。

public class Huffman {
private class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
char ch;
int freq;
boolean isLeaf;
Node left, right;
public Node(char ch, int freq) {
this.ch = ch;
this.freq = freq;
isLeaf = true;
}
public Node(Node left, Node right, int freq) {
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.freq = freq;
isLeaf = false;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.freq - o.freq;
}
}
public Map<Character, String> encode(Map<Character, Integer> frequencyForChar) {
PriorityQueue<Node> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (Character c : frequencyForChar.keySet()) {
priorityQueue.add(new Node(c, frequencyForChar.get(c)));
}
while (priorityQueue.size() != 1) {
Node node1 = priorityQueue.poll();
Node node2 = priorityQueue.poll();
priorityQueue.add(new Node(node1, node2, node1.freq + node2.freq));
}
return encode(priorityQueue.poll());
}
private Map<Character, String> encode(Node root) {
Map<Character, String> encodingForChar = new HashMap<>();
encode(root, "", encodingForChar);
return encodingForChar;
}
private void encode(Node node, String encoding, Map<Character, String> encodingForChar) {
if (node.isLeaf) {
encodingForChar.put(node.ch, encoding);
return;
}
encode(node.left, encoding + '0', encodingForChar);
encode(node.right, encoding + '1', encodingForChar);
}
}
