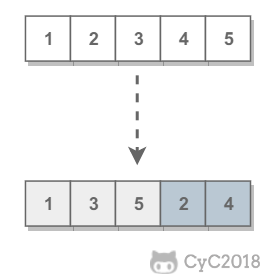
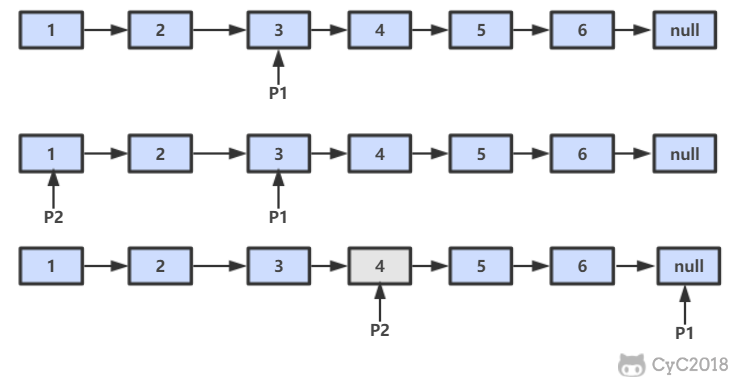
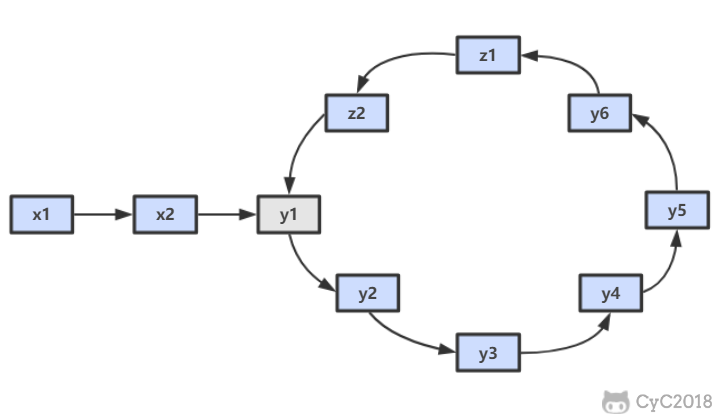
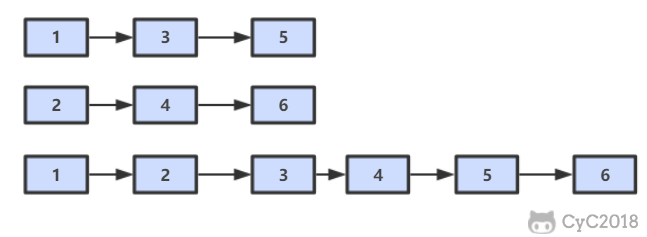
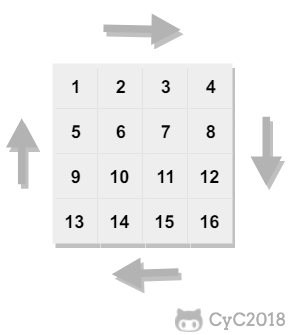
ret = new ArrayList<>();
int r1 = 0, r2 = matrix.length - 1, c1 = 0, c2 = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (r1 <= r2 && c1 <= c2) {
for (int i = c1; i <= c2; i++)
ret.add(matrix[r1][i]);
for (int i = r1 + 1; i <= r2; i++)
ret.add(matrix[i][c2]);
if (r1 != r2)
for (int i = c2 - 1; i >= c1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[r2][i]);
if (c1 != c2)
for (int i = r2 - 1; i > r1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[i][c1]);
r1++; r2--; c1++; c2--;
}
return ret;
}
```
🔔🔔🔔🔔🔔🔔🔔 更多精彩内容将发布在公众号 **CyC2018**,公众号提供了该项目的离线阅读版本,后台回复"下载" 即可领取。也提供了一份技术面试复习思维导图,不仅系统整理了面试知识点,而且标注了各个知识点的重要程度,从而帮你理清多而杂的面试知识点,后台回复"资料" 即可领取。我基本是按照这个思维导图来进行复习的,对我拿到了 BAT 头条等 Offer 起到很大的帮助。你们完全可以和我一样根据思维导图上列的知识点来进行复习,就不用看很多不重要的内容,也可以知道哪些内容很重要从而多安排一些复习时间。