* [概览](#概览)
* [1. List](#1-list)
* [2. Set](#2-set)
* [3. Queue](#3-queue)
* [4. Map](#4-map)
* [5. Java 1.0/1.1 容器](#5-java-1011-容器)
* [容器中的设计模式](#容器中的设计模式)
* [1. 迭代器模式](#1-迭代器模式)
* [2. 适配器模式](#2-适配器模式)
* [散列](#散列)
* [源码分析](#源码分析)
* [1. ArraList](#1-arralist)
* [2. Vector 与 Stack](#2-vector-与-stack)
* [3. LinkedList](#3-linkedlist)
* [4. TreeMap](#4-treemap)
* [5. HashMap](#5-hashmap)
* [6. LinkedHashMap](#6-linkedhashmap)
* [7. ConcurrentHashMap](#7-concurrenthashmap)
* [参考资料](#参考资料)
# 概览
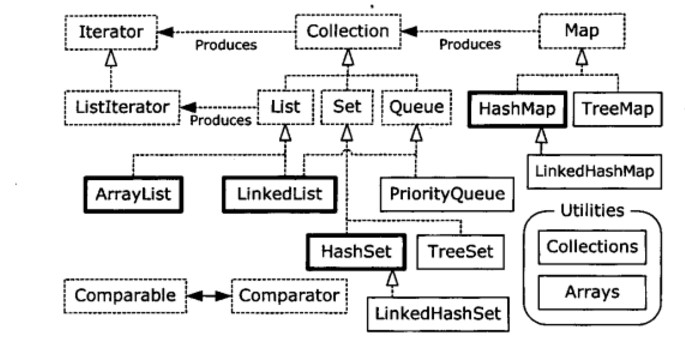
容器主要包括 Collection 和 Map 两种,Collection 又包含了 List、Set 以及 Queue。
## 1. List
- ArrayList:基于动态数组实现,支持随机访问;
- LinkedList:基于双向循环链表实现,只能顺序访问,但是可以快速地在链表中间插入和删除元素。不仅如此,LinkedList 还可以用作栈、队列和双端队列。
## 2. Set
- HashSet:基于 Hash 实现,支持快速查找,但是失去有序性;
- TreeSet:基于红黑树实现,保持有序,但是查找效率不如 HashSet;
- LinkedHashSet:具有 HashSet 的查找效率,且内部使用链表维护元素的插入顺序,因此具有有序性。
## 3. Queue
只有两个实现:LinkedList 和 PriorityQueue,其中 LinkedList 支持双向队列,PriorityQueue 是基于堆结构实现。
## 4. Map
- HashMap:基于 Hash 实现
- LinkedHashMap:使用链表来维护元素的顺序,顺序为插入顺序或者最近最少使用(LRU)顺序
- TreeMap:基于红黑树实现
- ConcurrentHashMap:线程安全 Map,不涉及类似于 HashTable 的同步加锁
## 5. Java 1.0/1.1 容器
对于旧的容器,我们决不应该使用它们,只需要对它们进行了解。
- Vector:和 ArrayList 类似,但它是线程安全的
- HashTable:和 HashMap 类似,但它是线程安全的
# 容器中的设计模式
## 1. 迭代器模式
从概览图可以看到,每个集合类都有一个 Iterator 对象,可以通过这个迭代器对象来遍历集合中的元素。
[Java 中的迭代器模式 ](https://github.com/CyC2018/InterviewNotes/blob/master/notes/%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1%E6%A8%A1%E5%BC%8F.md#92-java-%E5%86%85%E7%BD%AE%E7%9A%84%E8%BF%AD%E4%BB%A3%E5%99%A8)
## 2. 适配器模式
java.util.Arrays#asList() 可以把数组类型转换为 List 类型。
```java
List list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
list = Arrays.asList(arr);
```
# 散列
使用 hasCode() 来返回散列值,使用的是对象的地址。
而 equals() 是用来判断两个对象是否相等的,相等的两个对象散列值一定要相同,但是散列值相同的两个对象不一定相等。
相等必须满足以下五个性质:
1. 自反性
2. 对称性
3. 传递性
4. 一致性(多次调用 x.equals(y),结果不变)
5. 对任何不是 null 的对象 x 调用 x.equals(nul) 结果都为 false
# 源码分析
建议先阅读 [ 算法 - 查找 ](https://github.com/CyC2018/InterviewNotes/blob/master/notes/%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95.md#%E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%89%E7%AB%A0-%E6%9F%A5%E6%89%BE) 部分,对集合类源码的理解有很大帮助。
源码下载:[OpenJDK 1.7](http://download.java.net/openjdk/jdk7)
## 1. ArraList
[ArraList.java](https://github.com/CyC2018/JDK-Source-Code/tree/master/src/ArrayList.java)
实现了 RandomAccess 接口,因此支持随机访问,这是理所当然的,因为 ArrayList 是基于数组实现的。
```java
public class ArrayList extends AbstractList
implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
```
基于数组实现,保存元素的数组使用 transient 修饰,这是因为该数组不一定所有位置都占满元素,因此也就没必要全部都进行序列化。需要重写 writeObject() 和 readObject()。
```java
private transient Object[] elementData;
```
数组的默认大小为 10
```java
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
public ArrayList() {
this(10);
}
```
删除元素时调用 System.arraycopy() 对元素进行复制,因此删除操作成本很高,最好在创建时就指定大概的容量大小,减少复制操作的执行次数。
```java
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
```
添加元素时使用 ensureCapacity() 方法来保证容量足够,如果不够时,需要进行扩容,使得新容量为旧容量的 1.5 倍。
modCount 用来记录 ArrayList 结构发生变化的次数,因为每次在进行 add() 和 addAll() 时都需要调用 ensureCapacity(),因此直接在 ensureCapacity() 中对 modCount 进行修改。
结构发生变化:添加或者删除至少一个元素的所有操作,或者是调整内部数组的大小,仅仅只是设置元素的值不算结构发生变化。
```java
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > 0)
ensureCapacityInternal(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
```
在进行序列化或者迭代等操作时,需要比较操作前后 modCount 是否改变,如果改变了需要抛出 ConcurrentModificationException。
```java
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException{
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out array length
s.writeInt(elementData.length);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i()); 返回一个线程安全的 ArrayList,也可以使用 concurrent 并发包下的 CopyOnWriteArrayList 类;
**和 LinkedList 的区别**
1. ArrayList 基于动态数组实现,LinkedList 基于双向循环链表实现;
2. ArrayList 支持随机访问,LinkedList 不支持;
3. LinkedList 在任意位置添加删除元素更快。
## 2. Vector 与 Stack
[Vector.java](https://github.com/CyC2018/JDK-Source-Code/tree/master/src/Vector.java)
## 3. LinkedList
[LinkedList.java](https://github.com/CyC2018/JDK-Source-Code/tree/master/src/LinkedList.java)
## 4. TreeMap
[TreeMap.java](https://github.com/CyC2018/JDK-Source-Code/tree/master/src/TreeMap.java)
## 5. HashMap
[HashMap.java](https://github.com/CyC2018/JDK-Source-Code/tree/master/src/HashMap.java)
使用拉链法来解决冲突。
默认容量 capacity 为 16,需要注意的是容量必须保证为 2 的次方。容量就是 Entry[] table 数组的长度,size 是数组的实际使用量。
threshold 规定了一个 size 的临界值,size 必须小于 threshold,如果大于等于,就必须进行扩容操作。
threshold = capacity * load_factor,其中 load_factor 为 table 数组能够使用的比例,load_factor 过大会导致聚簇的出现,从而影响查询和插入的效率,详见算法笔记。
```java
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
transient Entry[] table;
transient int size;
int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
transient int modCount;
```
从下面的添加元素代码中可以看出,当需要扩容时,令 capacity 为原来的两倍。
```java
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
```
Entry 用来表示一个键值对元素,其中的 next 指针在序列化时会使用。
```java
static class Entry implements Map.Entry {
final K key;
V value;
Entry next;
final int hash;
}
```
get() 操作需要分成两种情况,key 为 null 和 不为 null,从中可以看出 HashMap 允许插入 null 作为键。
```java
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
```
put() 操作也需要根据 key 是否为 null 做不同的处理,需要注意的是如果本来没有 key 为 null 的键值对,新插入一个 key 为 null 的键值对时默认是放在数组的 0 位置,这是因为 null 不能计算 hash 值,也就无法知道应该放在哪个链表上。
```java
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
```
```java
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
```
## 6. LinkedHashMap
[LinkedHashMap.java](https://github.com/CyC2018/JDK-Source-Code/tree/master/src/HashMap.java)
## 7. ConcurrentHashMap
[ConcurrentHashMap.java](https://github.com/CyC2018/JDK-Source-Code/tree/master/src/HashMap.java)
[ 探索 ConcurrentHashMap 高并发性的实现机制 ](https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/java-lo-concurrenthashmap/)
# 参考资料
- Java 编程思想

