diff --git a/notes/HTTP.md b/notes/HTTP.md
index 243dc283..537b24fe 100644
--- a/notes/HTTP.md
+++ b/notes/HTTP.md
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@
* [二进制分帧层](#二进制分帧层)
* [服务端推送](#服务端推送)
* [首部压缩](#首部压缩)
-* [八、GET 和 POST 的区别](#八get-和-post-的区别)
+* [八、GET 和 POST 比较](#八get-和-post-比较)
* [作用](#作用)
* [参数](#参数)
* [安全](#安全)
@@ -61,13 +61,13 @@
## URL
-- URI(Uniform Resource Identifier,统一资源标识符)
-- URL(Uniform Resource Locator,统一资源定位符)
-- URN(Uniform Resource Name,统一资源名称),例如 urn:isbn:0-486-27557-4。
-
URI 包含 URL 和 URN,目前 WEB 只有 URL 比较流行,所以见到的基本都是 URL。
- 
+- URI(Uniform Resource Identifier,统一资源标识符)
+- URL(Uniform Resource Locator,统一资源定位符)
+- URN(Uniform Resource Name,统一资源名称)
+
+ 
## 请求和响应报文
@@ -197,7 +197,7 @@ CONNECT www.example.com:443 HTTP/1.1
- **204 No Content** :请求已经成功处理,但是返回的响应报文不包含实体的主体部分。一般在只需要从客户端往服务器发送信息,而不需要返回数据时使用。
-- **206 Partial Content** :表示客户端进行了范围请求。响应报文包含由 Content-Range 指定范围的实体内容。
+- **206 Partial Content** :表示客户端进行了范围请求,响应报文包含由 Content-Range 指定范围的实体内容。
## 3XX 重定向
@@ -219,7 +219,7 @@ CONNECT www.example.com:443 HTTP/1.1
- **401 Unauthorized** :该状态码表示发送的请求需要有认证信息(BASIC 认证、DIGEST 认证)。如果之前已进行过一次请求,则表示用户认证失败。
-- **403 Forbidden** :请求被拒绝,服务器端没有必要给出拒绝的详细理由。
+- **403 Forbidden** :请求被拒绝。
- **404 Not Found**
@@ -331,7 +331,7 @@ Set-Cookie: tasty_cookie=strawberry
[page content]
```
-客户端之后对同一个服务器发送请求时,会从浏览器中读出 Cookie 信息通过 Cookie 请求首部字段发送给服务器。
+客户端之后对同一个服务器发送请求时,会从浏览器中取出 Cookie 信息并通过 Cookie 请求首部字段发送给服务器。
```html
GET /sample_page.html HTTP/1.1
@@ -382,9 +382,9 @@ Path 标识指定了主机下的哪些路径可以接受 Cookie(该 URL 路径
除了可以将用户信息通过 Cookie 存储在用户浏览器中,也可以利用 Session 存储在服务器端,存储在服务器端的信息更加安全。
-Session 可以存储在服务器上的文件、数据库或者内存中。也可以将 Session 存储在内存型数据库中,比如 Redis,效率会更高。
+Session 可以存储在服务器上的文件、数据库或者内存中。也可以将 Session 存储在 Redis 这种内存型数据库中,效率会更高。
-使用 Session 维护用户登录的过程如下:
+使用 Session 维护用户登录状态的过程如下:
- 用户进行登录时,用户提交包含用户名和密码的表单,放入 HTTP 请求报文中;
- 服务器验证该用户名和密码;
@@ -499,7 +499,7 @@ If-Modified-Since: Wed, 21 Oct 2015 07:28:00 GMT
### 1. 短连接与长连接
-当浏览器访问一个包含多张图片的 HTML 页面时,除了请求访问 HTML 页面资源,还会请求图片资源。如果每进行一次 HTTP 通信就要断开一次 TCP 连接,连接建立和断开的开销会很大。
+当浏览器访问一个包含多张图片的 HTML 页面时,除了请求访问 HTML 页面资源,还会请求图片资源。如果每进行一次 HTTP 通信就要新建一个 TCP 连接,那么开销会很大。
长连接只需要建立一次 TCP 连接就能进行多次 HTTP 通信。
@@ -688,7 +688,7 @@ HTTPs 并不是新协议,而是让 HTTP 先和 SSL(Secure Sockets Layer)
### 3. HTTPs 采用的加密方式
-HTTPs 采用混合的加密机制,使用非对称密钥加密用于传输对称密钥来保证安全性,之后使用对称密钥加密进行通信来保证效率。(下图中的 Session Key 就是对称密钥)
+HTTPs 采用混合的加密机制,使用非对称密钥加密用于传输对称密钥来保证传输过程的安全性,之后使用对称密钥加密进行通信来保证通信过程的效率。(下图中的 Session Key 就是对称密钥)

@@ -717,7 +717,7 @@ HTTPs 的报文摘要功能之所以安全,是因为它结合了加密和认
## HTTPs 的缺点
- 因为需要进行加密解密等过程,因此速度会更慢;
-- 需要支付证书授权的高费用。
+- 需要支付证书授权的高额费用。
## 配置 HTTPs
@@ -727,7 +727,7 @@ HTTPs 的报文摘要功能之所以安全,是因为它结合了加密和认
## HTTP/1.x 缺陷
- HTTP/1.x 实现简单是以牺牲应用性能为代价的:
+ HTTP/1.x 实现简单是以牺牲性能为代价的:
- 客户端需要使用多个连接才能实现并发和缩短延迟;
- 不会压缩请求和响应首部,从而导致不必要的网络流量;
@@ -763,7 +763,7 @@ HTTP/2.0 要求客户端和服务器同时维护和更新一个包含之前见

-# 八、GET 和 POST 的区别
+# 八、GET 和 POST 比较
## 作用
@@ -870,6 +870,7 @@ DELETE /idX/delete HTTP/1.1 -> Returns 404
- [MDN : HTTP](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP)
- [HTTP/2 简介](https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/performance/http2/?hl=zh-cn)
- [htmlspecialchars](http://php.net/manual/zh/function.htmlspecialchars.php)
+- [Difference between file URI and URL in java](http://java2db.com/java-io/how-to-get-and-the-difference-between-file-uri-and-url-in-java)
- [How to Fix SQL Injection Using Java PreparedStatement & CallableStatement](https://software-security.sans.org/developer-how-to/fix-sql-injection-in-java-using-prepared-callable-statement)
- [浅谈 HTTP 中 Get 与 Post 的区别](https://www.cnblogs.com/hyddd/archive/2009/03/31/1426026.html)
- [Are http:// and www really necessary?](https://www.webdancers.com/are-http-and-www-necesary/)
diff --git a/notes/Leetcode 题解.md b/notes/Leetcode 题解.md
index 293f4328..102fe9b6 100644
--- a/notes/Leetcode 题解.md
+++ b/notes/Leetcode 题解.md
@@ -33,10 +33,6 @@
* [多数投票问题](#多数投票问题)
* [其它](#其它)
* [数据结构相关](#数据结构相关)
- * [栈和队列](#栈和队列)
- * [哈希表](#哈希表)
- * [字符串](#字符串)
- * [数组与矩阵](#数组与矩阵)
* [链表](#链表)
* [树](#树)
* [递归](#递归)
@@ -44,6 +40,10 @@
* [前中后序遍历](#前中后序遍历)
* [BST](#bst)
* [Trie](#trie)
+ * [栈和队列](#栈和队列)
+ * [哈希表](#哈希表)
+ * [字符串](#字符串)
+ * [数组与矩阵](#数组与矩阵)
* [图](#图)
* [二分图](#二分图)
* [拓扑排序](#拓扑排序)
@@ -2371,7 +2371,9 @@ public List diffWaysToCompute(String input) {
题目描述:有 N 阶楼梯,每次可以上一阶或者两阶,求有多少种上楼梯的方法。
-定义一个数组 dp 存储上楼梯的方法数(为了方便讨论,数组下标从 1 开始),dp[i] 表示走到第 i 个楼梯的方法数目。第 i 个楼梯可以从第 i-1 和 i-2 个楼梯再走一步到达,走到第 i 个楼梯的方法数为走到第 i-1 和第 i-2 个楼梯的方法数之和。
+定义一个数组 dp 存储上楼梯的方法数(为了方便讨论,数组下标从 1 开始),dp[i] 表示走到第 i 个楼梯的方法数目。
+
+第 i 个楼梯可以从第 i-1 和 i-2 个楼梯再走一步到达,走到第 i 个楼梯的方法数为走到第 i-1 和第 i-2 个楼梯的方法数之和。
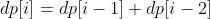
@@ -2400,7 +2402,9 @@ public int climbStairs(int n) {
题目描述:抢劫一排住户,但是不能抢邻近的住户,求最大抢劫量。
-定义 dp 数组用来存储最大的抢劫量,其中 dp[i] 表示抢到第 i 个住户时的最大抢劫量。由于不能抢劫邻近住户,因此如果抢劫了第 i 个住户那么只能抢劫 i - 2 或者 i - 3 的住户,所以
+定义 dp 数组用来存储最大的抢劫量,其中 dp[i] 表示抢到第 i 个住户时的最大抢劫量。
+
+由于不能抢劫邻近住户,因此如果抢劫了第 i 个住户那么只能抢劫 i - 2 或者 i - 3 的住户,所以
+nums[i])
@@ -4032,973 +4036,6 @@ public int maximumProduct(int[] nums) {
# 数据结构相关
-## 栈和队列
-
-**用栈实现队列**
-
-[232. Implement Queue using Stacks (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/description/)
-
-```java
-class MyQueue {
-
- private Stack in = new Stack<>();
- private Stack out = new Stack<>();
-
- public void push(int x) {
- in.push(x);
- }
-
- public int pop() {
- in2out();
- return out.pop();
- }
-
- public int peek() {
- in2out();
- return out.peek();
- }
-
- private void in2out() {
- if (out.isEmpty()) {
- while (!in.isEmpty()) {
- out.push(in.pop());
- }
- }
- }
-
- public boolean empty() {
- return in.isEmpty() && out.isEmpty();
- }
-}
-```
-
-**用队列实现栈**
-
-[225. Implement Stack using Queues (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/description/)
-
-在将一个元素 x 插入队列时,需要让除了 x 之外的所有元素出队列,再入队列。此时 x 在队首,第一个出队列,实现了后进先出顺序。
-
-```java
-class MyStack {
-
- private Queue queue;
-
- public MyStack() {
- queue = new LinkedList<>();
- }
-
- public void push(int x) {
- queue.add(x);
- int cnt = queue.size();
- while (cnt-- > 1) {
- queue.add(queue.poll());
- }
- }
-
- public int pop() {
- return queue.remove();
- }
-
- public int top() {
- return queue.peek();
- }
-
- public boolean empty() {
- return queue.isEmpty();
- }
-}
-```
-
-**最小值栈**
-
-[155. Min Stack (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/min-stack/description/)
-
-```java
-class MinStack {
-
- private Stack dataStack;
- private Stack minStack;
- private int min;
-
- public MinStack() {
- dataStack = new Stack<>();
- minStack = new Stack<>();
- min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- }
-
- public void push(int x) {
- dataStack.add(x);
- min = Math.min(min, x);
- minStack.add(min);
- }
-
- public void pop() {
- dataStack.pop();
- minStack.pop();
- min = minStack.isEmpty() ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : minStack.peek();
- }
-
- public int top() {
- return dataStack.peek();
- }
-
- public int getMin() {
- return minStack.peek();
- }
-}
-```
-
-对于实现最小值队列问题,可以先将队列使用栈来实现,然后就将问题转换为最小值栈,这个问题出现在 编程之美:3.7。
-
-**用栈实现括号匹配**
-
-[20. Valid Parentheses (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-parentheses/description/)
-
-```html
-"()[]{}"
-
-Output : true
-```
-
-```java
-public boolean isValid(String s) {
- Stack stack = new Stack<>();
- for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
- if (c == '(' || c == '{' || c == '[') {
- stack.push(c);
- } else {
- if (stack.isEmpty()) {
- return false;
- }
- char cStack = stack.pop();
- boolean b1 = c == ')' && cStack != '(';
- boolean b2 = c == ']' && cStack != '[';
- boolean b3 = c == '}' && cStack != '{';
- if (b1 || b2 || b3) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- }
- return stack.isEmpty();
-}
-```
-
-**数组中元素与下一个比它大的元素之间的距离**
-
-[739. Daily Temperatures (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/daily-temperatures/description/)
-
-```html
-Input: [73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73]
-Output: [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]
-```
-
-在遍历数组时用 Stack 把数组中的数存起来,如果当前遍历的数比栈顶元素来的大,说明栈顶元素的下一个比它大的数就是当前元素。
-
-```java
-public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
- int n = temperatures.length;
- int[] dist = new int[n];
- Stack indexs = new Stack<>();
- for (int curIndex = 0; curIndex < n; curIndex++) {
- while (!indexs.isEmpty() && temperatures[curIndex] > temperatures[indexs.peek()]) {
- int preIndex = indexs.pop();
- dist[preIndex] = curIndex - preIndex;
- }
- indexs.add(curIndex);
- }
- return dist;
-}
-```
-
-**循环数组中比当前元素大的下一个元素**
-
-[503. Next Greater Element II (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/next-greater-element-ii/description/)
-
-```text
-Input: [1,2,1]
-Output: [2,-1,2]
-Explanation: The first 1's next greater number is 2;
-The number 2 can't find next greater number;
-The second 1's next greater number needs to search circularly, which is also 2.
-```
-
-与 739. Daily Temperatures (Medium) 不同的是,数组是循环数组,并且最后要求的不是距离而是下一个元素。
-
-```java
-public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
- int n = nums.length;
- int[] next = new int[n];
- Arrays.fill(next, -1);
- Stack pre = new Stack<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++) {
- int num = nums[i % n];
- while (!pre.isEmpty() && nums[pre.peek()] < num) {
- next[pre.pop()] = num;
- }
- if (i < n){
- pre.push(i);
- }
- }
- return next;
-}
-```
-
-## 哈希表
-
-哈希表使用 O(N) 空间复杂度存储数据,从而能够以 O(1) 时间复杂度求解问题。
-
-Java 中的 **HashSet** 用于存储一个集合,可以查找元素是否在集合中。
-
-如果元素有穷,并且范围不大,那么可以用一个布尔数组来存储一个元素是否存在。例如对于只有小写字符的元素,就可以用一个长度为 26 的布尔数组来存储一个字符集合,使得空间复杂度降低为 O(1)。
-
-Java 中的 **HashMap** 主要用于映射关系,从而把两个元素联系起来。
-
-在对一个内容进行压缩或者其它转换时,利用 HashMap 可以把原始内容和转换后的内容联系起来。例如在一个简化 url 的系统中[Leetcdoe : 535. Encode and Decode TinyURL (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/encode-and-decode-tinyurl/description/),利用 HashMap 就可以存储精简后的 url 到原始 url 的映射,使得不仅可以显示简化的 url,也可以根据简化的 url 得到原始 url 从而定位到正确的资源。
-
-HashMap 也可以用来对元素进行计数统计,此时键为元素,值为计数。和 HashSet 类似,如果元素有穷并且范围不大,可以用整型数组来进行统计。
-
-**数组中的两个数和为给定值**
-
-[1. Two Sum (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/description/)
-
-可以先对数组进行排序,然后使用双指针方法或者二分查找方法。这样做的时间复杂度为 O(NlogN),空间复杂度为 O(1)。
-
-用 HashMap 存储数组元素和索引的映射,在访问到 nums[i] 时,判断 HashMap 中是否存在 target - nums[i],如果存在说明 target - nums[i] 所在的索引和 i 就是要找的两个数。该方法的时间复杂度为 O(N),空间复杂度为 O(N),使用空间来换取时间。
-
-```java
-public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
- HashMap indexForNum = new HashMap<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- if (indexForNum.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
- return new int[]{indexForNum.get(target - nums[i]), i};
- } else {
- indexForNum.put(nums[i], i);
- }
- }
- return null;
-}
-```
-
-**判断数组是否含有重复元素**
-
-[217. Contains Duplicate (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/contains-duplicate/description/)
-
-```java
-public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
- Set set = new HashSet<>();
- for (int num : nums) {
- set.add(num);
- }
- return set.size() < nums.length;
-}
-```
-
-**最长和谐序列**
-
-[594. Longest Harmonious Subsequence (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-harmonious-subsequence/description/)
-
-```html
-Input: [1,3,2,2,5,2,3,7]
-Output: 5
-Explanation: The longest harmonious subsequence is [3,2,2,2,3].
-```
-
-和谐序列中最大数和最小数只差正好为 1,应该注意的是序列的元素不一定是数组的连续元素。
-
-```java
-public int findLHS(int[] nums) {
- Map countForNum = new HashMap<>();
- for (int num : nums) {
- countForNum.put(num, countForNum.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
- }
- int longest = 0;
- for (int num : countForNum.keySet()) {
- if (countForNum.containsKey(num + 1)) {
- longest = Math.max(longest, countForNum.get(num + 1) + countForNum.get(num));
- }
- }
- return longest;
-}
-```
-
-**最长连续序列**
-
-[128. Longest Consecutive Sequence (Hard)](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence/description/)
-
-```html
-Given [100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2],
-The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Return its length: 4.
-```
-
-要求以 O(N) 的时间复杂度求解。
-
-```java
-public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
- Map countForNum = new HashMap<>();
- for (int num : nums) {
- countForNum.put(num, 1);
- }
- for (int num : nums) {
- forward(countForNum, num);
- }
- return maxCount(countForNum);
-}
-
-private int forward(Map countForNum, int num) {
- if (!countForNum.containsKey(num)) {
- return 0;
- }
- int cnt = countForNum.get(num);
- if (cnt > 1) {
- return cnt;
- }
- cnt = forward(countForNum, num + 1) + 1;
- countForNum.put(num, cnt);
- return cnt;
-}
-
-private int maxCount(Map countForNum) {
- int max = 0;
- for (int num : countForNum.keySet()) {
- max = Math.max(max, countForNum.get(num));
- }
- return max;
-}
-```
-
-## 字符串
-
-**两个字符串包含的字符是否完全相同**
-
-[242. Valid Anagram (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-anagram/description/)
-
-```html
-s = "anagram", t = "nagaram", return true.
-s = "rat", t = "car", return false.
-```
-
-字符串只包含小写字符,总共有 26 个小写字符。可以用 HashMap 来映射字符与出现次数。因为键的范围很小,因此可以使用长度为 26 的整型数组对字符串出现的字符进行统计,然后比较两个字符串出现的字符数量是否相同。
-
-```java
-public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
- int[] cnts = new int[26];
- for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
- cnts[c - 'a']++;
- }
- for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
- cnts[c - 'a']--;
- }
- for (int cnt : cnts) {
- if (cnt != 0) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
-}
-```
-
-**计算一组字符集合可以组成的回文字符串的最大长度**
-
-[409. Longest Palindrome (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindrome/description/)
-
-```html
-Input : "abccccdd"
-Output : 7
-Explanation : One longest palindrome that can be built is "dccaccd", whose length is 7.
-```
-
-使用长度为 256 的整型数组来统计每个字符出现的个数,每个字符有偶数个可以用来构成回文字符串。
-
-因为回文字符串最中间的那个字符可以单独出现,所以如果有单独的字符就把它放到最中间。
-
-```java
-public int longestPalindrome(String s) {
- int[] cnts = new int[256];
- for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
- cnts[c]++;
- }
- int palindrome = 0;
- for (int cnt : cnts) {
- palindrome += (cnt / 2) * 2;
- }
- if (palindrome < s.length()) {
- palindrome++; // 这个条件下 s 中一定有单个未使用的字符存在,可以把这个字符放到回文的最中间
- }
- return palindrome;
-}
-```
-
-**字符串同构**
-
-[205. Isomorphic Strings (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/description/)
-
-```html
-Given "egg", "add", return true.
-Given "foo", "bar", return false.
-Given "paper", "title", return true.
-```
-
-记录一个字符上次出现的位置,如果两个字符串中的字符上次出现的位置一样,那么就属于同构。
-
-```java
-public boolean isIsomorphic(String s, String t) {
- int[] preIndexOfS = new int[256];
- int[] preIndexOfT = new int[256];
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- char sc = s.charAt(i), tc = t.charAt(i);
- if (preIndexOfS[sc] != preIndexOfT[tc]) {
- return false;
- }
- preIndexOfS[sc] = i + 1;
- preIndexOfT[tc] = i + 1;
- }
- return true;
-}
-```
-
-**回文子字符串**
-
-[647. Palindromic Substrings (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/palindromic-substrings/description/)
-
-```html
-Input: "aaa"
-Output: 6
-Explanation: Six palindromic strings: "a", "a", "a", "aa", "aa", "aaa".
-```
-
-从字符串的某一位开始,尝试着去扩展子字符串。
-
-```java
-private int cnt = 0;
-
-public int countSubstrings(String s) {
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- extendSubstrings(s, i, i); // 奇数长度
- extendSubstrings(s, i, i + 1); // 偶数长度
- }
- return cnt;
-}
-
-private void extendSubstrings(String s, int start, int end) {
- while (start >= 0 && end < s.length() && s.charAt(start) == s.charAt(end)) {
- start--;
- end++;
- cnt++;
- }
-}
-```
-
-**判断一个整数是否是回文数**
-
-[9. Palindrome Number (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-number/description/)
-
-要求不能使用额外空间,也就不能将整数转换为字符串进行判断。
-
-将整数分成左右两部分,右边那部分需要转置,然后判断这两部分是否相等。
-
-```java
-public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
- if (x == 0) {
- return true;
- }
- if (x < 0 || x % 10 == 0) {
- return false;
- }
- int right = 0;
- while (x > right) {
- right = right * 10 + x % 10;
- x /= 10;
- }
- return x == right || x == right / 10;
-}
-```
-
-**统计二进制字符串中连续 1 和连续 0 数量相同的子字符串个数**
-
-[696. Count Binary Substrings (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-binary-substrings/description/)
-
-```html
-Input: "00110011"
-Output: 6
-Explanation: There are 6 substrings that have equal number of consecutive 1's and 0's: "0011", "01", "1100", "10", "0011", and "01".
-```
-
-```java
-public int countBinarySubstrings(String s) {
- int preLen = 0, curLen = 1, count = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
- if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i - 1)) {
- curLen++;
- } else {
- preLen = curLen;
- curLen = 1;
- }
-
- if (preLen >= curLen) {
- count++;
- }
- }
- return count;
-}
-```
-
-**字符串循环移位包含**
-
-[编程之美:3.1](#)
-
-```html
-s1 = AABCD, s2 = CDAA
-Return : true
-```
-
-给定两个字符串 s1 和 s2,要求判定 s2 是否能够被 s1 做循环移位得到的字符串包含。
-
-s1 进行循环移位的结果是 s1s1 的子字符串,因此只要判断 s2 是否是 s1s1 的子字符串即可。
-
-**字符串循环移位**
-
-[编程之美:2.17](#)
-
-```html
-s = "abcd123" k = 3
-Return "123abcd"
-```
-
-将字符串向右循环移动 k 位。
-
-将 abcd123 中的 abcd 和 123 单独逆序,得到 dcba321,然后对整个字符串进行逆序,得到 123abcd。
-
-**字符串中单词的翻转**
-
-[程序员代码面试指南](#)
-
-```html
-s = "I am a student"
-return "student a am I"
-```
-
-将每个单词逆序,然后将整个字符串逆序。
-
-## 数组与矩阵
-
-**把数组中的 0 移到末尾**
-
-[283. Move Zeroes (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-zeroes/description/)
-
-```html
-For example, given nums = [0, 1, 0, 3, 12], after calling your function, nums should be [1, 3, 12, 0, 0].
-```
-
-```java
-public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
- int idx = 0;
- for (int num : nums) {
- if (num != 0) {
- nums[idx++] = num;
- }
- }
- while (idx < nums.length) {
- nums[idx++] = 0;
- }
-}
-```
-
-**改变矩阵维度**
-
-[566. Reshape the Matrix (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/reshape-the-matrix/description/)
-
-```html
-Input:
-nums =
-[[1,2],
- [3,4]]
-r = 1, c = 4
-
-Output:
-[[1,2,3,4]]
-
-Explanation:
-The row-traversing of nums is [1,2,3,4]. The new reshaped matrix is a 1 * 4 matrix, fill it row by row by using the previous list.
-```
-
-```java
-public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
- int m = nums.length, n = nums[0].length;
- if (m * n != r * c) {
- return nums;
- }
- int[][] reshapedNums = new int[r][c];
- int index = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
- reshapedNums[i][j] = nums[index / n][index % n];
- index++;
- }
- }
- return reshapedNums;
-}
-```
-
-**找出数组中最长的连续 1**
-
-[485. Max Consecutive Ones (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-consecutive-ones/description/)
-
-```java
-public int findMaxConsecutiveOnes(int[] nums) {
- int max = 0, cur = 0;
- for (int x : nums) {
- cur = x == 0 ? 0 : cur + 1;
- max = Math.max(max, cur);
- }
- return max;
-}
-```
-
-**一个数组元素在 [1, n] 之间,其中一个数被替换为另一个数,找出重复的数和丢失的数**
-
-[645. Set Mismatch (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/set-mismatch/description/)
-
-```html
-Input: nums = [1,2,2,4]
-Output: [2,3]
-```
-
-```html
-Input: nums = [1,2,2,4]
-Output: [2,3]
-```
-
-最直接的方法是先对数组进行排序,这种方法时间复杂度为 O(NlogN)。本题可以以 O(N) 的时间复杂度、O(1) 空间复杂度来求解。
-
-主要思想是通过交换数组元素,使得数组上的元素在正确的位置上。遍历数组,如果第 i 位上的元素不是 i + 1,那么一直交换第 i 位和 nums[i] - 1 位置上的元素。
-
-```java
-public int[] findErrorNums(int[] nums) {
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- while (nums[i] != i + 1 && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i]) {
- swap(nums, i, nums[i] - 1);
- }
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- if (nums[i] != i + 1) {
- return new int[]{nums[i], i + 1};
- }
- }
- return null;
-}
-
-private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
- int tmp = nums[i];
- nums[i] = nums[j];
- nums[j] = tmp;
-}
-```
-
-类似题目:
-
-- [448. Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-numbers-disappeared-in-an-array/description/),寻找所有丢失的元素
-- [442. Find All Duplicates in an Array (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-duplicates-in-an-array/description/),寻找所有重复的元素。
-
-**找出数组中重复的数,数组值在 [1, n] 之间**
-
-[287. Find the Duplicate Number (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-duplicate-number/description/)
-
-要求不能修改数组,也不能使用额外的空间。
-
-二分查找解法:
-
-```java
-public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
- int l = 1, h = nums.length - 1;
- while (l <= h) {
- int mid = l + (h - l) / 2;
- int cnt = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- if (nums[i] <= mid) cnt++;
- }
- if (cnt > mid) h = mid - 1;
- else l = mid + 1;
- }
- return l;
-}
-```
-
-双指针解法,类似于有环链表中找出环的入口:
-
-```java
-public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
- int slow = nums[0], fast = nums[nums[0]];
- while (slow != fast) {
- slow = nums[slow];
- fast = nums[nums[fast]];
- }
- fast = 0;
- while (slow != fast) {
- slow = nums[slow];
- fast = nums[fast];
- }
- return slow;
-}
-```
-
-**有序矩阵查找**
-
-[240. Search a 2D Matrix II (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix-ii/description/)
-
-```html
-[
- [ 1, 5, 9],
- [10, 11, 13],
- [12, 13, 15]
-]
-```
-
-```java
-public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
- if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) return false;
- int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
- int row = 0, col = n - 1;
- while (row < m && col >= 0) {
- if (target == matrix[row][col]) return true;
- else if (target < matrix[row][col]) col--;
- else row++;
- }
- return false;
-}
-```
-
-**有序矩阵的 Kth Element**
-
-[378. Kth Smallest Element in a Sorted Matrix ((Medium))](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-sorted-matrix/description/)
-
-```html
-matrix = [
- [ 1, 5, 9],
- [10, 11, 13],
- [12, 13, 15]
-],
-k = 8,
-
-return 13.
-```
-
-解题参考:[Share my thoughts and Clean Java Code](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-sorted-matrix/discuss/85173)
-
-二分查找解法:
-
-```java
-public int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) {
- int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
- int lo = matrix[0][0], hi = matrix[m - 1][n - 1];
- while(lo <= hi) {
- int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
- int cnt = 0;
- for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
- for(int j = 0; j < n && matrix[i][j] <= mid; j++) {
- cnt++;
- }
- }
- if(cnt < k) lo = mid + 1;
- else hi = mid - 1;
- }
- return lo;
-}
-```
-
-堆解法:
-
-```java
-public int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) {
- int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
- PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue();
- for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) pq.offer(new Tuple(0, j, matrix[0][j]));
- for(int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) { // 小根堆,去掉 k - 1 个堆顶元素,此时堆顶元素就是第 k 的数
- Tuple t = pq.poll();
- if(t.x == m - 1) continue;
- pq.offer(new Tuple(t.x + 1, t.y, matrix[t.x + 1][t.y]));
- }
- return pq.poll().val;
-}
-
-class Tuple implements Comparable {
- int x, y, val;
- public Tuple(int x, int y, int val) {
- this.x = x; this.y = y; this.val = val;
- }
-
- @Override
- public int compareTo(Tuple that) {
- return this.val - that.val;
- }
-}
-```
-
-**数组相邻差值的个数**
-
-[667. Beautiful Arrangement II (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/beautiful-arrangement-ii/description/)
-
-```html
-Input: n = 3, k = 2
-Output: [1, 3, 2]
-Explanation: The [1, 3, 2] has three different positive integers ranging from 1 to 3, and the [2, 1] has exactly 2 distinct integers: 1 and 2.
-```
-
-题目描述:数组元素为 1\~n 的整数,要求构建数组,使得相邻元素的差值不相同的个数为 k。
-
-让前 k+1 个元素构建出 k 个不相同的差值,序列为:1 k+1 2 k 3 k-1 ... k/2 k/2+1.
-
-```java
-public int[] constructArray(int n, int k) {
- int[] ret = new int[n];
- ret[0] = 1;
- for (int i = 1, interval = k; i <= k; i++, interval--) {
- ret[i] = i % 2 == 1 ? ret[i - 1] + interval : ret[i - 1] - interval;
- }
- for (int i = k + 1; i < n; i++) {
- ret[i] = i + 1;
- }
- return ret;
-}
-```
-
-**数组的度**
-
-[697. Degree of an Array (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/degree-of-an-array/description/)
-
-```html
-Input: [1,2,2,3,1,4,2]
-Output: 6
-```
-
-题目描述:数组的度定义为元素出现的最高频率,例如上面的数组度为 3。要求找到一个最小的子数组,这个子数组的度和原数组一样。
-
-```java
-public int findShortestSubArray(int[] nums) {
- Map numsCnt = new HashMap<>();
- Map numsLastIndex = new HashMap<>();
- Map numsFirstIndex = new HashMap<>();
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- int num = nums[i];
- numsCnt.put(num, numsCnt.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
- numsLastIndex.put(num, i);
- if (!numsFirstIndex.containsKey(num)) {
- numsFirstIndex.put(num, i);
- }
- }
- int maxCnt = 0;
- for (int num : nums) {
- maxCnt = Math.max(maxCnt, numsCnt.get(num));
- }
- int ret = nums.length;
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- int num = nums[i];
- int cnt = numsCnt.get(num);
- if (cnt != maxCnt) continue;
- ret = Math.min(ret, numsLastIndex.get(num) - numsFirstIndex.get(num) + 1);
- }
- return ret;
-}
-```
-
-**对角元素相等的矩阵**
-
-[766. Toeplitz Matrix (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/toeplitz-matrix/description/)
-
-```html
-1234
-5123
-9512
-
-In the above grid, the diagonals are "[9]", "[5, 5]", "[1, 1, 1]", "[2, 2, 2]", "[3, 3]", "[4]", and in each diagonal all elements are the same, so the answer is True.
-```
-
-```java
-public boolean isToeplitzMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
- for (int i = 0; i < matrix[0].length; i++) {
- if (!check(matrix, matrix[0][i], 0, i)) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
- if (!check(matrix, matrix[i][0], i, 0)) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
-}
-
-private boolean check(int[][] matrix, int expectValue, int row, int col) {
- if (row >= matrix.length || col >= matrix[0].length) {
- return true;
- }
- if (matrix[row][col] != expectValue) {
- return false;
- }
- return check(matrix, expectValue, row + 1, col + 1);
-}
-```
-
-**嵌套数组**
-
-[565. Array Nesting (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/array-nesting/description/)
-
-```html
-Input: A = [5,4,0,3,1,6,2]
-Output: 4
-Explanation:
-A[0] = 5, A[1] = 4, A[2] = 0, A[3] = 3, A[4] = 1, A[5] = 6, A[6] = 2.
-
-One of the longest S[K]:
-S[0] = {A[0], A[5], A[6], A[2]} = {5, 6, 2, 0}
-```
-
-题目描述:S[i] 表示一个集合,集合的第一个元素是 A[i],第二个元素是 A[A[i]],如此嵌套下去。求最大的 S[i]。
-
-```java
-public int arrayNesting(int[] nums) {
- int max = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
- int cnt = 0;
- for (int j = i; nums[j] != -1; ) {
- cnt++;
- int t = nums[j];
- nums[j] = -1; // 标记该位置已经被访问
- j = t;
-
- }
- max = Math.max(max, cnt);
- }
- return max;
-}
-```
-
-**分隔数组**
-
-[769. Max Chunks To Make Sorted (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-chunks-to-make-sorted/description/)
-
-```html
-Input: arr = [1,0,2,3,4]
-Output: 4
-Explanation:
-We can split into two chunks, such as [1, 0], [2, 3, 4].
-However, splitting into [1, 0], [2], [3], [4] is the highest number of chunks possible.
-```
-
-题目描述:分隔数组,使得对每部分排序后数组就为有序。
-
-```java
-public int maxChunksToSorted(int[] arr) {
- if (arr == null) return 0;
- int ret = 0;
- int right = arr[0];
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- right = Math.max(right, arr[i]);
- if (right == i) ret++;
- }
- return ret;
-}
-```
-
## 链表
链表是空节点,或者有一个值和一个指向下一个链表的指针,因此很多链表问题可以用递归来处理。
@@ -5032,7 +4069,10 @@ public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
}
```
-如果只是判断是否存在交点,那么就是另一个问题,即 [编程之美:3.6]() 的问题。有两种解法:把第一个链表的结尾连接到第二个链表的开头,看第二个链表是否存在环;或者直接比较两个链表的最后一个节点是否相同。
+如果只是判断是否存在交点,那么就是另一个问题,即 [编程之美 3.6]() 的问题。有两种解法:
+
+- 把第一个链表的结尾连接到第二个链表的开头,看第二个链表是否存在环;
+- 或者直接比较两个链表的最后一个节点是否相同。
**链表反转**
@@ -5097,7 +4137,7 @@ Given 1->1->2->3->3, return 1->2->3.
```java
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
- if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
+ if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
return head.val == head.next.val ? head.next : head;
}
@@ -5419,8 +4459,8 @@ Input:
3 2 1 3
/ \ \
5 4 7
+
Output:
-Merged tree:
3
/ \
4 5
@@ -5446,6 +4486,7 @@ public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
```html
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
+
5
/ \
4 8
@@ -5453,10 +4494,11 @@ Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
+
return true, as there exist a root-to-leaf path 5->4->11->2 which sum is 22.
```
-路径和定义为从 root 到 leaf 的所有节点的和
+路径和定义为从 root 到 leaf 的所有节点的和。
```java
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
@@ -5848,7 +4890,7 @@ public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
[145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/description/)
-前序遍历为 root -> left -> right,后序遍历为 left -> right -> root,可以修改前序遍历成为 root -> right -> left,那么这个顺序就和后序遍历正好相反。
+前序遍历为 root -> left -> right,后序遍历为 left -> right -> root。可以修改前序遍历成为 root -> right -> left,那么这个顺序就和后序遍历正好相反。
```java
public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
@@ -6106,7 +5148,7 @@ public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) return new TreeNode(head.val);
ListNode preMid = preMid(head);
- ListNode mid = preMid.next;
+ ListNode mid = preMid.next;
preMid.next = null; // 断开链表
TreeNode t = new TreeNode(mid.val);
t.left = sortedListToBST(head);
@@ -6222,7 +5264,7 @@ private void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
return [2].
```
-答案可能不止一个,也就是有多个值出现的次数一样多,并且是最大的。
+答案可能不止一个,也就是有多个值出现的次数一样多。
```java
private int curCnt = 1;
@@ -6392,6 +5434,974 @@ class MapSum {
}
```
+
+## 栈和队列
+
+**用栈实现队列**
+
+[232. Implement Queue using Stacks (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/description/)
+
+栈的顺序为后进先出,而队列的顺序为先进先出。使用两个栈实现队列,一个元素需要经过两个栈才能出队列,在经过第一个栈时元素顺序被反转,经过第二个栈时再次被反转,此时就是先进先出顺序。
+
+```java
+class MyQueue {
+
+ private Stack in = new Stack<>();
+ private Stack out = new Stack<>();
+
+ public void push(int x) {
+ in.push(x);
+ }
+
+ public int pop() {
+ in2out();
+ return out.pop();
+ }
+
+ public int peek() {
+ in2out();
+ return out.peek();
+ }
+
+ private void in2out() {
+ if (out.isEmpty()) {
+ while (!in.isEmpty()) {
+ out.push(in.pop());
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ public boolean empty() {
+ return in.isEmpty() && out.isEmpty();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+**用队列实现栈**
+
+[225. Implement Stack using Queues (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/description/)
+
+在将一个元素 x 插入队列时,为了维护原来的后进先出顺序,需要让 x 插入队列首部。而队列的默认插入顺序是队列尾部,因此在将 x 插入队列尾部之后,需要让除了 x 之外的所有元素出队列,再入队列。
+
+```java
+class MyStack {
+
+ private Queue queue;
+
+ public MyStack() {
+ queue = new LinkedList<>();
+ }
+
+ public void push(int x) {
+ queue.add(x);
+ int cnt = queue.size();
+ while (cnt-- > 1) {
+ queue.add(queue.poll());
+ }
+ }
+
+ public int pop() {
+ return queue.remove();
+ }
+
+ public int top() {
+ return queue.peek();
+ }
+
+ public boolean empty() {
+ return queue.isEmpty();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+**最小值栈**
+
+[155. Min Stack (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/min-stack/description/)
+
+```java
+class MinStack {
+
+ private Stack dataStack;
+ private Stack minStack;
+ private int min;
+
+ public MinStack() {
+ dataStack = new Stack<>();
+ minStack = new Stack<>();
+ min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ }
+
+ public void push(int x) {
+ dataStack.add(x);
+ min = Math.min(min, x);
+ minStack.add(min);
+ }
+
+ public void pop() {
+ dataStack.pop();
+ minStack.pop();
+ min = minStack.isEmpty() ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : minStack.peek();
+ }
+
+ public int top() {
+ return dataStack.peek();
+ }
+
+ public int getMin() {
+ return minStack.peek();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+对于实现最小值队列问题,可以先将队列使用栈来实现,然后就将问题转换为最小值栈,这个问题出现在 编程之美:3.7。
+
+**用栈实现括号匹配**
+
+[20. Valid Parentheses (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-parentheses/description/)
+
+```html
+"()[]{}"
+
+Output : true
+```
+
+```java
+public boolean isValid(String s) {
+ Stack stack = new Stack<>();
+ for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
+ if (c == '(' || c == '{' || c == '[') {
+ stack.push(c);
+ } else {
+ if (stack.isEmpty()) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ char cStack = stack.pop();
+ boolean b1 = c == ')' && cStack != '(';
+ boolean b2 = c == ']' && cStack != '[';
+ boolean b3 = c == '}' && cStack != '{';
+ if (b1 || b2 || b3) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return stack.isEmpty();
+}
+```
+
+**数组中元素与下一个比它大的元素之间的距离**
+
+[739. Daily Temperatures (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/daily-temperatures/description/)
+
+```html
+Input: [73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73]
+Output: [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]
+```
+
+在遍历数组时用栈把数组中的数存起来,如果当前遍历的数比栈顶元素来的大,说明栈顶元素的下一个比它大的数就是当前元素。
+
+```java
+public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
+ int n = temperatures.length;
+ int[] dist = new int[n];
+ Stack indexs = new Stack<>();
+ for (int curIndex = 0; curIndex < n; curIndex++) {
+ while (!indexs.isEmpty() && temperatures[curIndex] > temperatures[indexs.peek()]) {
+ int preIndex = indexs.pop();
+ dist[preIndex] = curIndex - preIndex;
+ }
+ indexs.add(curIndex);
+ }
+ return dist;
+}
+```
+
+**循环数组中比当前元素大的下一个元素**
+
+[503. Next Greater Element II (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/next-greater-element-ii/description/)
+
+```text
+Input: [1,2,1]
+Output: [2,-1,2]
+Explanation: The first 1's next greater number is 2;
+The number 2 can't find next greater number;
+The second 1's next greater number needs to search circularly, which is also 2.
+```
+
+与 739. Daily Temperatures (Medium) 不同的是,数组是循环数组,并且最后要求的不是距离而是下一个元素。
+
+```java
+public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ int[] next = new int[n];
+ Arrays.fill(next, -1);
+ Stack pre = new Stack<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++) {
+ int num = nums[i % n];
+ while (!pre.isEmpty() && nums[pre.peek()] < num) {
+ next[pre.pop()] = num;
+ }
+ if (i < n){
+ pre.push(i);
+ }
+ }
+ return next;
+}
+```
+
+## 哈希表
+
+哈希表使用 O(N) 空间复杂度存储数据,并且以 O(1) 时间复杂度求解问题。
+
+- Java 中的 **HashSet** 用于存储一个集合,可以查找元素是否在集合中。如果元素有穷,并且范围不大,那么可以用一个布尔数组来存储一个元素是否存在。例如对于只有小写字符的元素,就可以用一个长度为 26 的布尔数组来存储一个字符集合,使得空间复杂度降低为 O(1)。
+
+- Java 中的 **HashMap** 主要用于映射关系,从而把两个元素联系起来。HashMap 也可以用来对元素进行计数统计,此时键为元素,值为计数。和 HashSet 类似,如果元素有穷并且范围不大,可以用整型数组来进行统计。在对一个内容进行压缩或者其它转换时,利用 HashMap 可以把原始内容和转换后的内容联系起来。例如在一个简化 url 的系统中 [Leetcdoe : 535. Encode and Decode TinyURL (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/encode-and-decode-tinyurl/description/),利用 HashMap 就可以存储精简后的 url 到原始 url 的映射,使得不仅可以显示简化的 url,也可以根据简化的 url 得到原始 url 从而定位到正确的资源。
+
+
+**数组中两个数的和为给定值**
+
+[1. Two Sum (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/description/)
+
+可以先对数组进行排序,然后使用双指针方法或者二分查找方法。这样做的时间复杂度为 O(NlogN),空间复杂度为 O(1)。
+
+用 HashMap 存储数组元素和索引的映射,在访问到 nums[i] 时,判断 HashMap 中是否存在 target - nums[i],如果存在说明 target - nums[i] 所在的索引和 i 就是要找的两个数。该方法的时间复杂度为 O(N),空间复杂度为 O(N),使用空间来换取时间。
+
+```java
+public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
+ HashMap indexForNum = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ if (indexForNum.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
+ return new int[]{indexForNum.get(target - nums[i]), i};
+ } else {
+ indexForNum.put(nums[i], i);
+ }
+ }
+ return null;
+}
+```
+
+**判断数组是否含有重复元素**
+
+[217. Contains Duplicate (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/contains-duplicate/description/)
+
+```java
+public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
+ Set set = new HashSet<>();
+ for (int num : nums) {
+ set.add(num);
+ }
+ return set.size() < nums.length;
+}
+```
+
+**最长和谐序列**
+
+[594. Longest Harmonious Subsequence (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-harmonious-subsequence/description/)
+
+```html
+Input: [1,3,2,2,5,2,3,7]
+Output: 5
+Explanation: The longest harmonious subsequence is [3,2,2,2,3].
+```
+
+和谐序列中最大数和最小数只差正好为 1,应该注意的是序列的元素不一定是数组的连续元素。
+
+```java
+public int findLHS(int[] nums) {
+ Map countForNum = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int num : nums) {
+ countForNum.put(num, countForNum.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
+ }
+ int longest = 0;
+ for (int num : countForNum.keySet()) {
+ if (countForNum.containsKey(num + 1)) {
+ longest = Math.max(longest, countForNum.get(num + 1) + countForNum.get(num));
+ }
+ }
+ return longest;
+}
+```
+
+**最长连续序列**
+
+[128. Longest Consecutive Sequence (Hard)](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence/description/)
+
+```html
+Given [100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2],
+The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Return its length: 4.
+```
+
+要求以 O(N) 的时间复杂度求解。
+
+```java
+public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
+ Map countForNum = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int num : nums) {
+ countForNum.put(num, 1);
+ }
+ for (int num : nums) {
+ forward(countForNum, num);
+ }
+ return maxCount(countForNum);
+}
+
+private int forward(Map countForNum, int num) {
+ if (!countForNum.containsKey(num)) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ int cnt = countForNum.get(num);
+ if (cnt > 1) {
+ return cnt;
+ }
+ cnt = forward(countForNum, num + 1) + 1;
+ countForNum.put(num, cnt);
+ return cnt;
+}
+
+private int maxCount(Map countForNum) {
+ int max = 0;
+ for (int num : countForNum.keySet()) {
+ max = Math.max(max, countForNum.get(num));
+ }
+ return max;
+}
+```
+
+## 字符串
+
+**字符串循环移位包含**
+
+[编程之美 3.1](#)
+
+```html
+s1 = AABCD, s2 = CDAA
+Return : true
+```
+
+给定两个字符串 s1 和 s2,要求判定 s2 是否能够被 s1 做循环移位得到的字符串包含。
+
+s1 进行循环移位的结果是 s1s1 的子字符串,因此只要判断 s2 是否是 s1s1 的子字符串即可。
+
+**字符串循环移位**
+
+[编程之美 2.17](#)
+
+```html
+s = "abcd123" k = 3
+Return "123abcd"
+```
+
+将字符串向右循环移动 k 位。
+
+将 abcd123 中的 abcd 和 123 单独翻转,得到 dcba321,然后对整个字符串进行翻转,得到 123abcd。
+
+**字符串中单词的翻转**
+
+[程序员代码面试指南](#)
+
+```html
+s = "I am a student"
+Return "student a am I"
+```
+
+将每个单词翻转,然后将整个字符串翻转。
+
+**两个字符串包含的字符是否完全相同**
+
+[242. Valid Anagram (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-anagram/description/)
+
+```html
+s = "anagram", t = "nagaram", return true.
+s = "rat", t = "car", return false.
+```
+
+可以用 HashMap 来映射字符与出现次数,然后比较两个字符串出现的字符数量是否相同。
+
+由于本题的字符串只包含 26 个小写字符,因此可以使用长度为 26 的整型数组对字符串出现的字符进行统计,不再使用 HashMap。
+
+```java
+public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
+ int[] cnts = new int[26];
+ for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
+ cnts[c - 'a']++;
+ }
+ for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
+ cnts[c - 'a']--;
+ }
+ for (int cnt : cnts) {
+ if (cnt != 0) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ }
+ return true;
+}
+```
+
+**计算一组字符集合可以组成的回文字符串的最大长度**
+
+[409. Longest Palindrome (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindrome/description/)
+
+```html
+Input : "abccccdd"
+Output : 7
+Explanation : One longest palindrome that can be built is "dccaccd", whose length is 7.
+```
+
+使用长度为 256 的整型数组来统计每个字符出现的个数,每个字符有偶数个可以用来构成回文字符串。
+
+因为回文字符串最中间的那个字符可以单独出现,所以如果有单独的字符就把它放到最中间。
+
+```java
+public int longestPalindrome(String s) {
+ int[] cnts = new int[256];
+ for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
+ cnts[c]++;
+ }
+ int palindrome = 0;
+ for (int cnt : cnts) {
+ palindrome += (cnt / 2) * 2;
+ }
+ if (palindrome < s.length()) {
+ palindrome++; // 这个条件下 s 中一定有单个未使用的字符存在,可以把这个字符放到回文的最中间
+ }
+ return palindrome;
+}
+```
+
+**字符串同构**
+
+[205. Isomorphic Strings (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/description/)
+
+```html
+Given "egg", "add", return true.
+Given "foo", "bar", return false.
+Given "paper", "title", return true.
+```
+
+记录一个字符上次出现的位置,如果两个字符串中的字符上次出现的位置一样,那么就属于同构。
+
+```java
+public boolean isIsomorphic(String s, String t) {
+ int[] preIndexOfS = new int[256];
+ int[] preIndexOfT = new int[256];
+ for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
+ char sc = s.charAt(i), tc = t.charAt(i);
+ if (preIndexOfS[sc] != preIndexOfT[tc]) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ preIndexOfS[sc] = i + 1;
+ preIndexOfT[tc] = i + 1;
+ }
+ return true;
+}
+```
+
+**回文子字符串个数**
+
+[647. Palindromic Substrings (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/palindromic-substrings/description/)
+
+```html
+Input: "aaa"
+Output: 6
+Explanation: Six palindromic strings: "a", "a", "a", "aa", "aa", "aaa".
+```
+
+从字符串的某一位开始,尝试着去扩展子字符串。
+
+```java
+private int cnt = 0;
+
+public int countSubstrings(String s) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
+ extendSubstrings(s, i, i); // 奇数长度
+ extendSubstrings(s, i, i + 1); // 偶数长度
+ }
+ return cnt;
+}
+
+private void extendSubstrings(String s, int start, int end) {
+ while (start >= 0 && end < s.length() && s.charAt(start) == s.charAt(end)) {
+ start--;
+ end++;
+ cnt++;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+**判断一个整数是否是回文数**
+
+[9. Palindrome Number (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-number/description/)
+
+要求不能使用额外空间,也就不能将整数转换为字符串进行判断。
+
+将整数分成左右两部分,右边那部分需要转置,然后判断这两部分是否相等。
+
+```java
+public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
+ if (x == 0) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ if (x < 0 || x % 10 == 0) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ int right = 0;
+ while (x > right) {
+ right = right * 10 + x % 10;
+ x /= 10;
+ }
+ return x == right || x == right / 10;
+}
+```
+
+**统计二进制字符串中连续 1 和连续 0 数量相同的子字符串个数**
+
+[696. Count Binary Substrings (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-binary-substrings/description/)
+
+```html
+Input: "00110011"
+Output: 6
+Explanation: There are 6 substrings that have equal number of consecutive 1's and 0's: "0011", "01", "1100", "10", "0011", and "01".
+```
+
+```java
+public int countBinarySubstrings(String s) {
+ int preLen = 0, curLen = 1, count = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
+ if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i - 1)) {
+ curLen++;
+ } else {
+ preLen = curLen;
+ curLen = 1;
+ }
+
+ if (preLen >= curLen) {
+ count++;
+ }
+ }
+ return count;
+}
+```
+
+## 数组与矩阵
+
+**把数组中的 0 移到末尾**
+
+[283. Move Zeroes (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-zeroes/description/)
+
+```html
+For example, given nums = [0, 1, 0, 3, 12], after calling your function, nums should be [1, 3, 12, 0, 0].
+```
+
+```java
+public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
+ int idx = 0;
+ for (int num : nums) {
+ if (num != 0) {
+ nums[idx++] = num;
+ }
+ }
+ while (idx < nums.length) {
+ nums[idx++] = 0;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+**改变矩阵维度**
+
+[566. Reshape the Matrix (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/reshape-the-matrix/description/)
+
+```html
+Input:
+nums =
+[[1,2],
+ [3,4]]
+r = 1, c = 4
+
+Output:
+[[1,2,3,4]]
+
+Explanation:
+The row-traversing of nums is [1,2,3,4]. The new reshaped matrix is a 1 * 4 matrix, fill it row by row by using the previous list.
+```
+
+```java
+public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
+ int m = nums.length, n = nums[0].length;
+ if (m * n != r * c) {
+ return nums;
+ }
+ int[][] reshapedNums = new int[r][c];
+ int index = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
+ reshapedNums[i][j] = nums[index / n][index % n];
+ index++;
+ }
+ }
+ return reshapedNums;
+}
+```
+
+**找出数组中最长的连续 1**
+
+[485. Max Consecutive Ones (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-consecutive-ones/description/)
+
+```java
+public int findMaxConsecutiveOnes(int[] nums) {
+ int max = 0, cur = 0;
+ for (int x : nums) {
+ cur = x == 0 ? 0 : cur + 1;
+ max = Math.max(max, cur);
+ }
+ return max;
+}
+```
+
+**有序矩阵查找**
+
+[240. Search a 2D Matrix II (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix-ii/description/)
+
+```html
+[
+ [ 1, 5, 9],
+ [10, 11, 13],
+ [12, 13, 15]
+]
+```
+
+```java
+public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
+ if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) return false;
+ int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
+ int row = 0, col = n - 1;
+ while (row < m && col >= 0) {
+ if (target == matrix[row][col]) return true;
+ else if (target < matrix[row][col]) col--;
+ else row++;
+ }
+ return false;
+}
+```
+
+**有序矩阵的 Kth Element**
+
+[378. Kth Smallest Element in a Sorted Matrix ((Medium))](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-sorted-matrix/description/)
+
+```html
+matrix = [
+ [ 1, 5, 9],
+ [10, 11, 13],
+ [12, 13, 15]
+],
+k = 8,
+
+return 13.
+```
+
+解题参考:[Share my thoughts and Clean Java Code](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-sorted-matrix/discuss/85173)
+
+二分查找解法:
+
+```java
+public int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) {
+ int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
+ int lo = matrix[0][0], hi = matrix[m - 1][n - 1];
+ while (lo <= hi) {
+ int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
+ int cnt = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < n && matrix[i][j] <= mid; j++) {
+ cnt++;
+ }
+ }
+ if (cnt < k) lo = mid + 1;
+ else hi = mid - 1;
+ }
+ return lo;
+}
+```
+
+堆解法:
+
+```java
+public int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) {
+ int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
+ PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue();
+ for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) pq.offer(new Tuple(0, j, matrix[0][j]));
+ for(int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) { // 小根堆,去掉 k - 1 个堆顶元素,此时堆顶元素就是第 k 的数
+ Tuple t = pq.poll();
+ if(t.x == m - 1) continue;
+ pq.offer(new Tuple(t.x + 1, t.y, matrix[t.x + 1][t.y]));
+ }
+ return pq.poll().val;
+}
+
+class Tuple implements Comparable {
+ int x, y, val;
+ public Tuple(int x, int y, int val) {
+ this.x = x; this.y = y; this.val = val;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int compareTo(Tuple that) {
+ return this.val - that.val;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+**一个数组元素在 [1, n] 之间,其中一个数被替换为另一个数,找出重复的数和丢失的数**
+
+[645. Set Mismatch (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/set-mismatch/description/)
+
+```html
+Input: nums = [1,2,2,4]
+Output: [2,3]
+```
+
+```html
+Input: nums = [1,2,2,4]
+Output: [2,3]
+```
+
+最直接的方法是先对数组进行排序,这种方法时间复杂度为 O(NlogN)。本题可以以 O(N) 的时间复杂度、O(1) 空间复杂度来求解。
+
+主要思想是通过交换数组元素,使得数组上的元素在正确的位置上。
+
+```java
+public int[] findErrorNums(int[] nums) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ while (nums[i] != i + 1 && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i]) {
+ swap(nums, i, nums[i] - 1);
+ }
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ if (nums[i] != i + 1) {
+ return new int[]{nums[i], i + 1};
+ }
+ }
+ return null;
+}
+
+private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
+ int tmp = nums[i];
+ nums[i] = nums[j];
+ nums[j] = tmp;
+}
+```
+
+类似题目:
+
+- [448. Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-numbers-disappeared-in-an-array/description/),寻找所有丢失的元素
+- [442. Find All Duplicates in an Array (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-duplicates-in-an-array/description/),寻找所有重复的元素。
+
+**找出数组中重复的数,数组值在 [1, n] 之间**
+
+[287. Find the Duplicate Number (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-duplicate-number/description/)
+
+要求不能修改数组,也不能使用额外的空间。
+
+二分查找解法:
+
+```java
+public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
+ int l = 1, h = nums.length - 1;
+ while (l <= h) {
+ int mid = l + (h - l) / 2;
+ int cnt = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ if (nums[i] <= mid) cnt++;
+ }
+ if (cnt > mid) h = mid - 1;
+ else l = mid + 1;
+ }
+ return l;
+}
+```
+
+双指针解法,类似于有环链表中找出环的入口:
+
+```java
+public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
+ int slow = nums[0], fast = nums[nums[0]];
+ while (slow != fast) {
+ slow = nums[slow];
+ fast = nums[nums[fast]];
+ }
+ fast = 0;
+ while (slow != fast) {
+ slow = nums[slow];
+ fast = nums[fast];
+ }
+ return slow;
+}
+```
+
+**数组相邻差值的个数**
+
+[667. Beautiful Arrangement II (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/beautiful-arrangement-ii/description/)
+
+```html
+Input: n = 3, k = 2
+Output: [1, 3, 2]
+Explanation: The [1, 3, 2] has three different positive integers ranging from 1 to 3, and the [2, 1] has exactly 2 distinct integers: 1 and 2.
+```
+
+题目描述:数组元素为 1\~n 的整数,要求构建数组,使得相邻元素的差值不相同的个数为 k。
+
+让前 k+1 个元素构建出 k 个不相同的差值,序列为:1 k+1 2 k 3 k-1 ... k/2 k/2+1.
+
+```java
+public int[] constructArray(int n, int k) {
+ int[] ret = new int[n];
+ ret[0] = 1;
+ for (int i = 1, interval = k; i <= k; i++, interval--) {
+ ret[i] = i % 2 == 1 ? ret[i - 1] + interval : ret[i - 1] - interval;
+ }
+ for (int i = k + 1; i < n; i++) {
+ ret[i] = i + 1;
+ }
+ return ret;
+}
+```
+
+**数组的度**
+
+[697. Degree of an Array (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/degree-of-an-array/description/)
+
+```html
+Input: [1,2,2,3,1,4,2]
+Output: 6
+```
+
+题目描述:数组的度定义为元素出现的最高频率,例如上面的数组度为 3。要求找到一个最小的子数组,这个子数组的度和原数组一样。
+
+```java
+public int findShortestSubArray(int[] nums) {
+ Map numsCnt = new HashMap<>();
+ Map numsLastIndex = new HashMap<>();
+ Map numsFirstIndex = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ int num = nums[i];
+ numsCnt.put(num, numsCnt.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
+ numsLastIndex.put(num, i);
+ if (!numsFirstIndex.containsKey(num)) {
+ numsFirstIndex.put(num, i);
+ }
+ }
+ int maxCnt = 0;
+ for (int num : nums) {
+ maxCnt = Math.max(maxCnt, numsCnt.get(num));
+ }
+ int ret = nums.length;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ int num = nums[i];
+ int cnt = numsCnt.get(num);
+ if (cnt != maxCnt) continue;
+ ret = Math.min(ret, numsLastIndex.get(num) - numsFirstIndex.get(num) + 1);
+ }
+ return ret;
+}
+```
+
+**对角元素相等的矩阵**
+
+[766. Toeplitz Matrix (Easy)](https://leetcode.com/problems/toeplitz-matrix/description/)
+
+```html
+1234
+5123
+9512
+
+In the above grid, the diagonals are "[9]", "[5, 5]", "[1, 1, 1]", "[2, 2, 2]", "[3, 3]", "[4]", and in each diagonal all elements are the same, so the answer is True.
+```
+
+```java
+public boolean isToeplitzMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < matrix[0].length; i++) {
+ if (!check(matrix, matrix[0][i], 0, i)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
+ if (!check(matrix, matrix[i][0], i, 0)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ }
+ return true;
+}
+
+private boolean check(int[][] matrix, int expectValue, int row, int col) {
+ if (row >= matrix.length || col >= matrix[0].length) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ if (matrix[row][col] != expectValue) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ return check(matrix, expectValue, row + 1, col + 1);
+}
+```
+
+**嵌套数组**
+
+[565. Array Nesting (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/array-nesting/description/)
+
+```html
+Input: A = [5,4,0,3,1,6,2]
+Output: 4
+Explanation:
+A[0] = 5, A[1] = 4, A[2] = 0, A[3] = 3, A[4] = 1, A[5] = 6, A[6] = 2.
+
+One of the longest S[K]:
+S[0] = {A[0], A[5], A[6], A[2]} = {5, 6, 2, 0}
+```
+
+题目描述:S[i] 表示一个集合,集合的第一个元素是 A[i],第二个元素是 A[A[i]],如此嵌套下去。求最大的 S[i]。
+
+```java
+public int arrayNesting(int[] nums) {
+ int max = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
+ int cnt = 0;
+ for (int j = i; nums[j] != -1; ) {
+ cnt++;
+ int t = nums[j];
+ nums[j] = -1; // 标记该位置已经被访问
+ j = t;
+
+ }
+ max = Math.max(max, cnt);
+ }
+ return max;
+}
+```
+
+**分隔数组**
+
+[769. Max Chunks To Make Sorted (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-chunks-to-make-sorted/description/)
+
+```html
+Input: arr = [1,0,2,3,4]
+Output: 4
+Explanation:
+We can split into two chunks, such as [1, 0], [2, 3, 4].
+However, splitting into [1, 0], [2], [3], [4] is the highest number of chunks possible.
+```
+
+题目描述:分隔数组,使得对每部分排序后数组就为有序。
+
+```java
+public int maxChunksToSorted(int[] arr) {
+ if (arr == null) return 0;
+ int ret = 0;
+ int right = arr[0];
+ for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
+ right = Math.max(right, arr[i]);
+ if (right == i) ret++;
+ }
+ return ret;
+}
+```
+
+
## 图
### 二分图
@@ -7052,3 +7062,4 @@ public int[] countBits(int num) {
- 何海涛, 软件工程师. 剑指 Offer: 名企面试官精讲典型编程题[M]. 电子工业出版社, 2014.
- 《编程之美》小组. 编程之美[M]. 电子工业出版社, 2008.
- 左程云. 程序员代码面试指南[M]. 电子工业出版社, 2015.
+
diff --git a/notes/Linux.md b/notes/Linux.md
index ebcc347b..14d3b317 100644
--- a/notes/Linux.md
+++ b/notes/Linux.md
@@ -275,8 +275,6 @@ BIOS 不可以读取 GPT 分区表,而 UEFI 可以。
## 组成
- 
-
最主要的几个组成部分如下:
- inode:一个文件占用一个 inode,记录文件的属性,同时记录此文件的内容所在的 block 编号;
@@ -287,6 +285,9 @@ BIOS 不可以读取 GPT 分区表,而 UEFI 可以。
- superblock:记录文件系统的整体信息,包括 inode 和 block 的总量、使用量、剩余量,以及文件系统的格式与相关信息等;
- block bitmap:记录 block 是否被使用的位域;
+ 
+
+
## 文件读取
对于 Ext2 文件系统,当要读取一个文件的内容时,先在 inode 中去查找文件内容所在的所有 block,然后把所有 block 的内容读出来。
@@ -336,7 +337,9 @@ inode 中记录了文件内容所在的 block 编号,但是每个 block 非常
## 目录
-建立一个目录时,会分配一个 inode 与至少一个 block。block 记录的内容是目录下所有文件的 inode 编号以及文件名。可以看出文件的 inode 本身不记录文件名,文件名记录在目录中,因此新增文件、删除文件、更改文件名这些操作与目录的 w 权限有关。
+建立一个目录时,会分配一个 inode 与至少一个 block。block 记录的内容是目录下所有文件的 inode 编号以及文件名。
+
+可以看出文件的 inode 本身不记录文件名,文件名记录在目录中,因此新增文件、删除文件、更改文件名这些操作与目录的 w 权限有关。
## 日志
diff --git a/notes/MySQL.md b/notes/MySQL.md
index 1c575fae..690425db 100644
--- a/notes/MySQL.md
+++ b/notes/MySQL.md
@@ -139,7 +139,7 @@ B+ Tree 是基于 B Tree 和叶子节点顺序访问指针进行实现,它具
### 2. 操作
-操作时,首先在根节点进行二分查找,找到一个 key 所在的指针,然后递归地在指针所指向的节点进行查找。直到查找到叶子节点,然后在叶子节点上进行二分查找,找出 key 所对应的 data。
+进行查找操作时,首先在根节点进行二分查找,找到一个 key 所在的指针,然后递归地在指针所指向的节点进行查找。直到查找到叶子节点,然后在叶子节点上进行二分查找,找出 key 所对应的 data。
插入删除操作记录会破坏平衡树的平衡性,因此在插入删除时,需要对树进行一个分裂、合并、旋转等操作。
diff --git a/notes/剑指 offer 题解.md b/notes/剑指 offer 题解.md
index 47d5d94e..0c9bd1f9 100644
--- a/notes/剑指 offer 题解.md
+++ b/notes/剑指 offer 题解.md
@@ -633,11 +633,12 @@ public int RectCover(int n) {
## 解题思路
-当 nums[m] <= nums[h] 的情况下,说明解在 [l, m] 之间,此时令 h = m;否则解在 [m + 1, h] 之间,令 l = m + 1。
+- 当 nums[m] <= nums[h] 的情况下,说明解在 [l, m] 之间,此时令 h = m;
+- 否则解在 [m + 1, h] 之间,令 l = m + 1。
-因为 h 的赋值表达式为 h = m,因此循环体的循环条件应该为 l < h,详细解释请见 [Leetcode 题解](https://github.com/CyC2018/Interview-Notebook/blob/master/notes/Leetcode%20%E9%A2%98%E8%A7%A3.md#%E4%BA%8C%E5%88%86%E6%9F%A5%E6%89%BE) 二分查找部分。
+因为 h 的赋值表达式为 h = m,因此循环体的循环条件应该为 l < h,详细解释请见 [Leetcode 题解](https://github.com/CyC2018/Interview-Notebook/blob/master/notes/Leetcode%20%E9%A2%98%E8%A7%A3.md) 二分查找部分。
-但是如果出现 nums[l] == nums[m] == nums[h],那么此时无法确定解在哪个区间,因此需要切换到顺序查找。
+但是如果出现 nums[l] == nums[m] == nums[h],那么此时无法确定解在哪个区间,需要切换到顺序查找。
复杂度:O(logN) + O(1)
@@ -1217,8 +1218,7 @@ public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
### 递归
```java
-public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2)
-{
+public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null)
return list2;
if (list2 == null)
@@ -1236,8 +1236,7 @@ public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2)
### 迭代
```java
-public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2)
-{
+public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = head;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
@@ -1269,15 +1268,13 @@ public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2)
## 解题思路
```java
-public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2)
-{
+public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null || root2 == null)
return false;
return isSubtreeWithRoot(root1, root2) || HasSubtree(root1.left, root2) || HasSubtree(root1.right, root2);
}
-private boolean isSubtreeWithRoot(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2)
-{
+private boolean isSubtreeWithRoot(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root2 == null)
return true;
if (root1 == null)
@@ -1298,9 +1295,10 @@ private boolean isSubtreeWithRoot(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2)
## 解题思路
+### 递归
+
```java
-public void Mirror(TreeNode root)
-{
+public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
swap(root);
@@ -1308,14 +1306,36 @@ public void Mirror(TreeNode root)
Mirror(root.right);
}
-private void swap(TreeNode root)
-{
+private void swap(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode t = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = t;
}
```
+### 迭代
+
+```java
+public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
+ Stack stack = new Stack<>();
+ stack.push(root);
+ while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
+ TreeNode node = stack.pop();
+ if (node == null)
+ continue;
+ swap(node);
+ stack.push(node.left);
+ stack.push(node.right);
+ }
+}
+
+private void swap(TreeNode node) {
+ TreeNode t = node.left;
+ node.left = node.right;
+ node.right = t;
+}
+```
+
# 28 对称的二叉树
[NowCder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/ff05d44dfdb04e1d83bdbdab320efbcb?tpId=13&tqId=11211&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
@@ -1327,15 +1347,13 @@ private void swap(TreeNode root)
## 解题思路
```java
-boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot)
-{
+boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {
if (pRoot == null)
return true;
return isSymmetrical(pRoot.left, pRoot.right);
}
-boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2)
-{
+boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null)
return true;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null)
@@ -1359,8 +1377,7 @@ boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2)
## 解题思路
```java
-public ArrayList printMatrix(int[][] matrix)
-{
+public ArrayList printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
int r1 = 0, r2 = matrix.length - 1, c1 = 0, c2 = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (r1 <= r2 && c1 <= c2) {
@@ -1394,25 +1411,21 @@ public ArrayList printMatrix(int[][] matrix)
private Stack dataStack = new Stack<>();
private Stack minStack = new Stack<>();
-public void push(int node)
-{
+public void push(int node) {
dataStack.push(node);
minStack.push(minStack.isEmpty() ? node : Math.min(minStack.peek(), node));
}
-public void pop()
-{
+public void pop() {
dataStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
-public int top()
-{
+public int top() {
return dataStack.peek();
}
-public int min()
-{
+public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
```
@@ -1430,8 +1443,7 @@ public int min()
使用一个栈来模拟压入弹出操作。
```java
-public boolean IsPopOrder(int[] pushSequence, int[] popSequence)
-{
+public boolean IsPopOrder(int[] pushSequence, int[] popSequence) {
int n = pushSequence.length;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
for (int pushIndex = 0, popIndex = 0; pushIndex < n; pushIndex++) {
@@ -1464,8 +1476,7 @@ public boolean IsPopOrder(int[] pushSequence, int[] popSequence)
不需要使用两个队列分别存储当前层的节点和下一层的节点,因为在开始遍历一层的节点时,当前队列中的节点数就是当前层的节点数,只要控制遍历这么多节点数,就能保证这次遍历的都是当前层的节点。
```java
-public ArrayList PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root)
-{
+public ArrayList PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
queue.add(root);
@@ -1495,8 +1506,7 @@ public ArrayList PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root)
## 解题思路
```java
-ArrayList> Print(TreeNode pRoot)
-{
+ArrayList> Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(pRoot);
@@ -1529,8 +1539,7 @@ ArrayList> Print(TreeNode pRoot)
## 解题思路
```java
-public ArrayList> Print(TreeNode pRoot)
-{
+public ArrayList> Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(pRoot);
@@ -1571,15 +1580,13 @@ public ArrayList> Print(TreeNode pRoot)
## 解题思路
```java
-public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int[] sequence)
-{
+public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int[] sequence) {
if (sequence == null || sequence.length == 0)
return false;
return verify(sequence, 0, sequence.length - 1);
}
-private boolean verify(int[] sequence, int first, int last)
-{
+private boolean verify(int[] sequence, int first, int last) {
if (last - first <= 1)
return true;
int rootVal = sequence[last];
@@ -1610,14 +1617,12 @@ private boolean verify(int[] sequence, int first, int last)
```java
private ArrayList> ret = new ArrayList<>();
-public ArrayList> FindPath(TreeNode root, int target)
-{
+public ArrayList> FindPath(TreeNode root, int target) {
backtracking(root, target, new ArrayList<>());
return ret;
}
-private void backtracking(TreeNode node, int target, ArrayList path)
-{
+private void backtracking(TreeNode node, int target, ArrayList path) {
if (node == null)
return;
path.add(node.val);
@@ -1641,8 +1646,7 @@ private void backtracking(TreeNode node, int target, ArrayList path)
输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的 head。
```java
-public class RandomListNode
-{
+public class RandomListNode {
int label;
RandomListNode next = null;
RandomListNode random = null;
@@ -1670,8 +1674,7 @@ public class RandomListNode

```java
-public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead)
-{
+public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null)
return null;
// 插入新节点
@@ -1718,14 +1721,12 @@ public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead)
private TreeNode pre = null;
private TreeNode head = null;
-public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode root)
-{
+public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode root) {
inOrder(root);
return head;
}
-private void inOrder(TreeNode node)
-{
+private void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null)
return;
inOrder(node.left);
@@ -1752,21 +1753,18 @@ private void inOrder(TreeNode node)
```java
private String deserializeStr;
-public String Serialize(TreeNode root)
-{
+public String Serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return "#";
return root.val + " " + Serialize(root.left) + " " + Serialize(root.right);
}
-public TreeNode Deserialize(String str)
-{
+public TreeNode Deserialize(String str) {
deserializeStr = str;
return Deserialize();
}
-private TreeNode Deserialize()
-{
+private TreeNode Deserialize() {
if (deserializeStr.length() == 0)
return null;
int index = deserializeStr.indexOf(" ");
@@ -1795,8 +1793,7 @@ private TreeNode Deserialize()
```java
private ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
-public ArrayList Permutation(String str)
-{
+public ArrayList Permutation(String str) {
if (str.length() == 0)
return ret;
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
@@ -1805,8 +1802,7 @@ public ArrayList Permutation(String str)
return ret;
}
-private void backtracking(char[] chars, boolean[] hasUsed, StringBuilder s)
-{
+private void backtracking(char[] chars, boolean[] hasUsed, StringBuilder s) {
if (s.length() == chars.length) {
ret.add(s.toString());
return;
@@ -1836,8 +1832,7 @@ private void backtracking(char[] chars, boolean[] hasUsed, StringBuilder s)
使用 cnt 来统计一个元素出现的次数,当遍历到的元素和统计元素不相等时,令 cnt--。如果前面查找了 i 个元素,且 cnt == 0,说明前 i 个元素没有 majority,或者有 majority,但是出现的次数少于 i / 2 ,因为如果多于 i / 2 的话 cnt 就一定不会为 0 。此时剩下的 n - i 个元素中,majority 的数目依然多于 (n - i) / 2,因此继续查找就能找出 majority。
```java
-public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int[] nums)
-{
+public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int[] nums) {
int majority = nums[0];
for (int i = 1, cnt = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
cnt = nums[i] == majority ? cnt + 1 : cnt - 1;
@@ -1868,8 +1863,7 @@ public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int[] nums)
快速排序的 partition() 方法,会返回一个整数 j 使得 a[l..j-1] 小于等于 a[j],且 a[j+1..h] 大于等于 a[j],此时 a[j] 就是数组的第 j 大元素。可以利用这个特性找出数组的第 K 个元素,这种找第 K 个元素的算法称为快速选择算法。
```java
-public ArrayList GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k)
-{
+public ArrayList GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) {
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (k > nums.length || k <= 0)
return ret;
@@ -1880,8 +1874,7 @@ public ArrayList GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k)
return ret;
}
-public void findKthSmallest(int[] nums, int k)
-{
+public void findKthSmallest(int[] nums, int k) {
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int j = partition(nums, l, h);
@@ -1894,8 +1887,7 @@ public void findKthSmallest(int[] nums, int k)
}
}
-private int partition(int[] nums, int l, int h)
-{
+private int partition(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
int p = nums[l]; /* 切分元素 */
int i = l, j = h + 1;
while (true) {
@@ -1909,8 +1901,7 @@ private int partition(int[] nums, int l, int h)
return j;
}
-private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j)
-{
+private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
@@ -1927,8 +1918,7 @@ private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j)
维护一个大小为 K 的最小堆过程如下:在添加一个元素之后,如果大顶堆的大小大于 K,那么需要将大顶堆的堆顶元素去除。
```java
-public ArrayList GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k)
-{
+public ArrayList GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) {
if (k > nums.length || k <= 0)
return new ArrayList<>();
PriorityQueue maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);
@@ -1959,8 +1949,7 @@ private PriorityQueue right = new PriorityQueue<>();
/* 当前数据流读入的元素个数 */
private int N = 0;
-public void Insert(Integer val)
-{
+public void Insert(Integer val) {
/* 插入要保证两个堆存于平衡状态 */
if (N % 2 == 0) {
/* N 为偶数的情况下插入到右半边。
@@ -1975,8 +1964,7 @@ public void Insert(Integer val)
N++;
}
-public Double GetMedian()
-{
+public Double GetMedian() {
if (N % 2 == 0)
return (left.peek() + right.peek()) / 2.0;
else
@@ -1998,16 +1986,14 @@ public Double GetMedian()
private int[] cnts = new int[256];
private Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
-public void Insert(char ch)
-{
+public void Insert(char ch) {
cnts[ch]++;
queue.add(ch);
while (!queue.isEmpty() && cnts[queue.peek()] > 1)
queue.poll();
}
-public char FirstAppearingOnce()
-{
+public char FirstAppearingOnce() {
return queue.isEmpty() ? '#' : queue.peek();
}
```
@@ -2023,8 +2009,7 @@ public char FirstAppearingOnce()
## 解题思路
```java
-public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] nums)
-{
+public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return 0;
int greatestSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
@@ -2044,8 +2029,7 @@ public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] nums)
## 解题思路
```java
-public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n)
-{
+public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int m = 1; m <= n; m *= 10) {
int a = n / m, b = n % m;
@@ -2066,8 +2050,7 @@ public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n)
## 解题思路
```java
-public int getDigitAtIndex(int index)
-{
+public int getDigitAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0)
return -1;
int place = 1; // 1 表示个位,2 表示 十位...
@@ -2085,8 +2068,7 @@ public int getDigitAtIndex(int index)
* place 位数的数字组成的字符串长度
* 10, 90, 900, ...
*/
-private int getAmountOfPlace(int place)
-{
+private int getAmountOfPlace(int place) {
if (place == 1)
return 10;
return (int) Math.pow(10, place - 1) * 9;
@@ -2096,8 +2078,7 @@ private int getAmountOfPlace(int place)
* place 位数的起始数字
* 0, 10, 100, ...
*/
-private int getBeginNumberOfPlace(int place)
-{
+private int getBeginNumberOfPlace(int place) {
if (place == 1)
return 0;
return (int) Math.pow(10, place - 1);
@@ -2106,8 +2087,7 @@ private int getBeginNumberOfPlace(int place)
/**
* 在 place 位数组成的字符串中,第 index 个数
*/
-private int getDigitAtIndex(int index, int place)
-{
+private int getDigitAtIndex(int index, int place) {
int beginNumber = getBeginNumberOfPlace(place);
int shiftNumber = index / place;
String number = (beginNumber + shiftNumber) + "";
@@ -2129,8 +2109,7 @@ private int getDigitAtIndex(int index, int place)
可以看成是一个排序问题,在比较两个字符串 S1 和 S2 的大小时,应该比较的是 S1+S2 和 S2+S1 的大小,如果 S1+S2 < S2+S1,那么应该把 S1 排在前面,否则应该把 S2 排在前面。
```java
-public String PrintMinNumber(int[] numbers)
-{
+public String PrintMinNumber(int[] numbers) {
if (numbers == null || numbers.length == 0)
return "";
int n = numbers.length;
@@ -2156,8 +2135,7 @@ public String PrintMinNumber(int[] numbers)
## 解题思路
```java
-public int numDecodings(String s)
-{
+public int numDecodings(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0)
return 0;
int n = s.length();
@@ -2200,8 +2178,7 @@ public int numDecodings(String s)
应该用动态规划求解,而不是深度优先搜索,深度优先搜索过于复杂,不是最优解。
```java
-public int getMost(int[][] values)
-{
+public int getMost(int[][] values) {
if (values == null || values.length == 0 || values[0].length == 0)
return 0;
int n = values[0].length;
@@ -2224,8 +2201,7 @@ public int getMost(int[][] values)
## 解题思路
```java
-public int longestSubStringWithoutDuplication(String str)
-{
+public int longestSubStringWithoutDuplication(String str) {
int curLen = 0;
int maxLen = 0;
int[] preIndexs = new int[26];
@@ -2257,8 +2233,7 @@ public int longestSubStringWithoutDuplication(String str)
## 解题思路
```java
-public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int N)
-{
+public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int N) {
if (N <= 6)
return N;
int i2 = 0, i3 = 0, i5 = 0;
@@ -2291,8 +2266,7 @@ public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int N)
最直观的解法是使用 HashMap 对出现次数进行统计,但是考虑到要统计的字符范围有限,因此可以使用整型数组代替 HashMap。
```java
-public int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str)
-{
+public int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str) {
int[] cnts = new int[256];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
cnts[str.charAt(i)]++;
@@ -2306,8 +2280,7 @@ public int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str)
以上实现的空间复杂度还不是最优的。考虑到只需要找到只出现一次的字符,那么我们只需要统计的次数信息只有 0,1,更大,使用两个比特位就能存储这些信息。
```java
-public int FirstNotRepeatingChar2(String str)
-{
+public int FirstNotRepeatingChar2(String str) {
BitSet bs1 = new BitSet(256);
BitSet bs2 = new BitSet(256);
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
@@ -2339,15 +2312,13 @@ public int FirstNotRepeatingChar2(String str)
private long cnt = 0;
private int[] tmp; // 在这里创建辅助数组,而不是在 merge() 递归函数中创建
-public int InversePairs(int[] nums)
-{
+public int InversePairs(int[] nums) {
tmp = new int[nums.length];
mergeSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
return (int) (cnt % 1000000007);
}
-private void mergeSort(int[] nums, int l, int h)
-{
+private void mergeSort(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
if (h - l < 1)
return;
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
@@ -2356,8 +2327,7 @@ private void mergeSort(int[] nums, int l, int h)
merge(nums, l, m, h);
}
-private void merge(int[] nums, int l, int m, int h)
-{
+private void merge(int[] nums, int l, int m, int h) {
int i = l, j = m + 1, k = l;
while (i <= m || j <= h) {
if (i > m)
@@ -2392,8 +2362,7 @@ private void merge(int[] nums, int l, int m, int h)
当访问 A 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 B 的头部重新开始访问链表 B;同样地,当访问 B 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 A 的头部重新开始访问链表 A。这样就能控制访问 A 和 B 两个链表的指针能同时访问到交点。
```java
-public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2)
-{
+public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
ListNode l1 = pHead1, l2 = pHead2;
while (l1 != l2) {
l1 = (l1 == null) ? pHead2 : l1.next;
@@ -2420,15 +2389,13 @@ Output:
## 解题思路
```java
-public int GetNumberOfK(int[] nums, int K)
-{
+public int GetNumberOfK(int[] nums, int K) {
int first = binarySearch(nums, K);
int last = binarySearch(nums, K + 1);
return (first == nums.length || nums[first] != K) ? 0 : last - first;
}
-private int binarySearch(int[] nums, int K)
-{
+private int binarySearch(int[] nums, int K) {
int l = 0, h = nums.length;
while (l < h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
@@ -2453,14 +2420,12 @@ private int binarySearch(int[] nums, int K)
private TreeNode ret;
private int cnt = 0;
-public TreeNode KthNode(TreeNode pRoot, int k)
-{
+public TreeNode KthNode(TreeNode pRoot, int k) {
inOrder(pRoot, k);
return ret;
}
-private void inOrder(TreeNode root, int k)
-{
+private void inOrder(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null || cnt >= k)
return;
inOrder(root.left, k);
@@ -2484,8 +2449,7 @@ private void inOrder(TreeNode root, int k)
## 解题思路
```java
-public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root)
-{
+public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {
return root == null ? 0 : 1 + Math.max(TreeDepth(root.left), TreeDepth(root.right));
}
```
@@ -2505,14 +2469,12 @@ public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root)
```java
private boolean isBalanced = true;
-public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root)
-{
+public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
height(root);
return isBalanced;
}
-private int height(TreeNode root)
-{
+private int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null || !isBalanced)
return 0;
int left = height(root.left);
@@ -2538,8 +2500,7 @@ private int height(TreeNode root)
diff &= -diff 得到出 diff 最右侧不为 0 的位,也就是不存在重复的两个元素在位级表示上最右侧不同的那一位,利用这一位就可以将两个元素区分开来。
```java
-public void FindNumsAppearOnce(int[] nums, int num1[], int num2[])
-{
+public void FindNumsAppearOnce(int[] nums, int num1[], int num2[]) {
int diff = 0;
for (int num : nums)
diff ^= num;
@@ -2570,8 +2531,7 @@ public void FindNumsAppearOnce(int[] nums, int num1[], int num2[])
- 如果 sum < target,移动较小的元素,使 sum 变大一些。
```java
-public ArrayList FindNumbersWithSum(int[] array, int sum)
-{
+public ArrayList FindNumbersWithSum(int[] array, int sum) {
int i = 0, j = array.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
int cur = array[i] + array[j];
@@ -2604,8 +2564,7 @@ public ArrayList FindNumbersWithSum(int[] array, int sum)
## 解题思路
```java
-public ArrayList> FindContinuousSequence(int sum)
-{
+public ArrayList> FindContinuousSequence(int sum) {
ArrayList> ret = new ArrayList<>();
int start = 1, end = 2;
int curSum = 3;
@@ -2648,8 +2607,7 @@ public ArrayList> FindContinuousSequence(int sum)
正确的解法应该是和书上一样,先旋转每个单词,再旋转整个字符串。
```java
-public String ReverseSentence(String str)
-{
+public String ReverseSentence(String str) {
int n = str.length();
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int i = 0, j = 0;
@@ -2664,14 +2622,12 @@ public String ReverseSentence(String str)
return new String(chars);
}
-private void reverse(char[] c, int i, int j)
-{
+private void reverse(char[] c, int i, int j) {
while (i < j)
swap(c, i++, j--);
}
-private void swap(char[] c, int i, int j)
-{
+private void swap(char[] c, int i, int j) {
char t = c[i];
c[i] = c[j];
c[j] = t;
@@ -2691,8 +2647,7 @@ private void swap(char[] c, int i, int j)
先将 "abc" 和 "XYZdef" 分别翻转,得到 "cbafedZYX",然后再把整个字符串翻转得到 "XYZdefabc"。
```java
-public String LeftRotateString(String str, int n)
-{
+public String LeftRotateString(String str, int n) {
if (n >= str.length())
return str;
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
@@ -2702,14 +2657,12 @@ public String LeftRotateString(String str, int n)
return new String(chars);
}
-private void reverse(char[] chars, int i, int j)
-{
+private void reverse(char[] chars, int i, int j) {
while (i < j)
swap(chars, i++, j--);
}
-private void swap(char[] chars, int i, int j)
-{
+private void swap(char[] chars, int i, int j) {
char t = chars[i];
chars[i] = chars[j];
chars[j] = t;
@@ -2727,8 +2680,7 @@ private void swap(char[] chars, int i, int j)
## 解题思路
```java
-public ArrayList maxInWindows(int[] num, int size)
-{
+public ArrayList maxInWindows(int[] num, int size) {
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (size > num.length || size < 1)
return ret;
@@ -2762,8 +2714,7 @@ public ArrayList maxInWindows(int[] num, int size)
空间复杂度:O(N2)
```java
-public List> dicesSum(int n)
-{
+public List> dicesSum(int n) {
final int face = 6;
final int pointNum = face * n;
long[][] dp = new long[n + 1][pointNum + 1];
@@ -2790,8 +2741,7 @@ public List> dicesSum(int n)
空间复杂度:O(N)
```java
-public List> dicesSum(int n)
-{
+public List> dicesSum(int n) {
final int face = 6;
final int pointNum = face * n;
long[][] dp = new long[2][pointNum + 1];
@@ -2829,8 +2779,7 @@ public List> dicesSum(int n)
## 解题思路
```java
-public boolean isContinuous(int[] nums)
-{
+public boolean isContinuous(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length < 5)
return false;
Arrays.sort(nums);
@@ -2861,8 +2810,7 @@ public boolean isContinuous(int[] nums)
约瑟夫环,圆圈长度为 n 的解可以看成长度为 n-1 的解再加上报数的长度 m。因为是圆圈,所以最后需要对 n 取余。
```java
-public int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m)
-{
+public int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m) {
if (n == 0) /* 特殊输入的处理 */
return -1;
if (n == 1) /* 返回条件 */
@@ -2884,8 +2832,7 @@ public int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m)
使用贪心策略,假设第 i 轮进行卖出操作,买入操作价格应该在 i 之前并且价格最低。
```java
-public int maxProfit(int[] prices)
-{
+public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if (prices == null || prices.length == 0)
return 0;
int soFarMin = prices[0];
@@ -2915,8 +2862,7 @@ public int maxProfit(int[] prices)
以下实现中,递归的返回条件为 n <= 0,取非后就是 n > 0,递归的主体部分为 sum += Sum_Solution(n - 1),转换为条件语句后就是 (sum += Sum_Solution(n - 1)) > 0。
```java
-public int Sum_Solution(int n)
-{
+public int Sum_Solution(int n) {
int sum = n;
boolean b = (n > 0) && ((sum += Sum_Solution(n - 1)) > 0);
return sum;
@@ -2938,8 +2884,7 @@ a ^ b 表示没有考虑进位的情况下两数的和,(a & b) << 1 就是进
递归会终止的原因是 (a & b) << 1 最右边会多一个 0,那么继续递归,进位最右边的 0 会慢慢增多,最后进位会变为 0,递归终止。
```java
-public int Add(int a, int b)
-{
+public int Add(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : Add(a ^ b, (a & b) << 1);
}
```
@@ -2955,8 +2900,7 @@ public int Add(int a, int b)
## 解题思路
```java
-public int[] multiply(int[] A)
-{
+public int[] multiply(int[] A) {
int n = A.length;
int[] B = new int[n];
for (int i = 0, product = 1; i < n; product *= A[i], i++) /* 从左往右累乘 */
@@ -2988,8 +2932,7 @@ Output:
## 解题思路
```java
-public int StrToInt(String str)
-{
+public int StrToInt(String str) {
if (str == null || str.length() == 0)
return 0;
boolean isNegative = str.charAt(0) == '-';
diff --git a/notes/消息队列.md b/notes/消息队列.md
index e28fcd3f..74155802 100644
--- a/notes/消息队列.md
+++ b/notes/消息队列.md
@@ -46,17 +46,17 @@
例如在注册流程中通常需要发送验证邮件来确保注册用户的身份合法,可以使用消息队列使发送验证邮件的操作异步处理,用户在填写完注册信息之后就可以完成注册,而将发送验证邮件这一消息发送到消息队列中。
-只有在业务流程允许异步处理的情况下才能这么做,例如上面的注册流程中,如果要求用户对验证邮件进行点击之后才能完成操作的话,就不能再使用消息队列。
+只有在业务流程允许异步处理的情况下才能这么做,例如上面的注册流程中,如果要求用户对验证邮件进行点击之后才能完成注册的话,就不能再使用消息队列。
## 流量削锋
-在高并发的场景下,如果短时间有大量的请求会压垮服务器。
+在高并发的场景下,如果短时间有大量的请求到达会压垮服务器。
可以将请求发送到消息队列中,服务器按照其处理能力从消息队列中订阅消息进行处理。
## 应用解耦
-如果模块之间不直接进行调用,模块之间耦合度很低,那么修改一个模块或者新增一个模块对其它模块的影响会很小,从而实现可扩展性。
+如果模块之间不直接进行调用,模块之间耦合度就会很低,那么修改一个模块或者新增一个模块对其它模块的影响会很小,从而实现可扩展性。
通过使用消息队列,一个模块只需要向消息队列中发送消息,其它模块可以选择性地从消息队列中订阅消息从而完成调用。
diff --git a/notes/算法.md b/notes/算法.md
index fb878742..cb5d4dbe 100644
--- a/notes/算法.md
+++ b/notes/算法.md
@@ -1623,10 +1623,10 @@ private List keys(Node x, Key l, Key h) {
## 2-3 查找树
-
-
2-3 查找树引入了 2- 节点和 3- 节点,目的是为了让树平衡。一颗完美平衡的 2-3 查找树的所有空链接到根节点的距离应该是相同的。
+
+
### 1. 插入操作
插入操作和 BST 的插入操作有很大区别,BST 的插入操作是先进行一次未命中的查找,然后再将节点插入到对应的空链接上。但是 2-3 查找树如果也这么做的话,那么就会破坏了平衡性。它是将新节点插入到叶子节点上。
@@ -2042,24 +2042,26 @@ public class SparseVector {
## 汉诺塔
+
+
这是一个经典的递归问题,分为三步求解:
-1. 将 n-1 个圆盘从 from -> buffer
-2. 将 1 个圆盘从 from -> to
-3. 将 n-1 个圆盘从 buffer -> to
+- 将 n-1 个圆盘从 from -> buffer
+
+
+
+- 将 1 个圆盘从 from -> to
+
+
+
+- 将 n-1 个圆盘从 buffer -> to
+
+
如果只有一个圆盘,那么只需要进行一次移动操作。
从上面的讨论可以知道,an = 2 * an-1 + 1,显然 an = 2n - 1,n 个圆盘需要移动 2n - 1 次。
- 
-
- 
-
- 
-
- 
-
```java
public class Hanoi {
public static void move(int n, String from, String buffer, String to) {
@@ -2105,7 +2107,7 @@ from H1 to H3
生成编码时,从根节点出发,向左遍历则添加二进制位 0,向右则添加二进制位 1,直到遍历到根节点,根节点代表的字符的编码就是这个路径编码。
- 
+ 
```java
public class Huffman {
diff --git a/notes/缓存.md b/notes/缓存.md
index e60373dd..449598ff 100644
--- a/notes/缓存.md
+++ b/notes/缓存.md
@@ -163,7 +163,11 @@ public class LRU implements Iterable {
## 分布式缓存
-使用 Redis、Memcache 等分布式缓存将数据缓存在分布式缓存系统中。相对于本地缓存来说,分布式缓存单独部署,可以根据需求分配硬件资源。不仅如此,服务器集群都可以访问分布式缓存,本地缓存需要在服务器集群之间进行同步,实现和性能开销上都非常大。
+使用 Redis、Memcache 等分布式缓存将数据缓存在分布式缓存系统中。
+
+相对于本地缓存来说,分布式缓存单独部署,可以根据需求分配硬件资源。
+
+不仅如此,服务器集群都可以访问分布式缓存。而本地缓存需要在服务器集群之间进行同步,实现和性能开销上都非常大。
## 数据库缓存
@@ -171,7 +175,7 @@ MySQL 等数据库管理系统具有自己的查询缓存机制来提高 SQL 查
# 四、CDN
-内容分发网络(Content distribution network,CDN)是一种通过互连的网络系统,利用更靠近用户的服务器更快更可靠地将 HTML、CSS、JavaScript、音乐、图片、视频等静态资源其它数据分发给用户。
+内容分发网络(Content distribution network,CDN)是一种通过互连的网络系统,利用更靠近用户的服务器更快更可靠地将 HTML、CSS、JavaScript、音乐、图片、视频等静态资源分发给用户。
CDN 主要有以下优点:
@@ -190,7 +194,7 @@ CDN 主要有以下优点:
## 缓存穿透
-指的是对某个一定不存在的数据进行请求,该请求将会穿透缓存来到数据库。
+指的是对某个一定不存在的数据进行请求,该请求将会穿透缓存到达数据库。
解决方案:
@@ -207,6 +211,7 @@ CDN 主要有以下优点:
- 为了防止缓存在同一时间大面积过期导致的缓存雪崩,可以通过观察用户行为,合理设置缓存过期时间来实现;
- 为了防止缓存服务器宕机出现的缓存雪崩,可以使用分布式缓存,分布式缓存中每一个节点只缓存部分的数据,当某个节点宕机时可以保证其它节点的缓存仍然可用。
+- 也可以在进行缓存预热,避免在系统刚启动不久由于还未将大量数据进行缓存而导致缓存雪崩。
## 缓存一致性
@@ -258,7 +263,7 @@ Distributed Hash Table(DHT) 是一种哈希分布方式,其目的是为了
上面描述的一致性哈希存在数据分布不均匀的问题,节点存储的数据量有可能会存在很大的不同。
-数据不均匀主要是因为节点在哈希环上分布的不均匀,这种情况在节点数量很少的情况下尤其明显。解决方式是通过增加虚拟节点,然后将虚拟节点映射到真实节点上。虚拟节点的数量比真实节点来得大,那么虚拟节点在哈希环上分布的均匀性就会比原来的真是节点号,从而使得数据分布也更加均匀。
+数据不均匀主要是因为节点在哈希环上分布的不均匀,这种情况在节点数量很少的情况下尤其明显。解决方式是通过增加虚拟节点,然后将虚拟节点映射到真实节点上。虚拟节点的数量比真实节点来得大,那么虚拟节点在哈希环上分布的均匀性就会比原来的真是节点好,从而使得数据分布也更加均匀。
参考资料:
diff --git a/notes/设计模式.md b/notes/设计模式.md
index ae44213e..d48d7b36 100644
--- a/notes/设计模式.md
+++ b/notes/设计模式.md
@@ -1851,11 +1851,7 @@ No gumball dispensed
### 与状态模式的比较
-状态模式的类图和策略模式类似,并且都是能够动态改变对象的行为。
-
-但是状态模式是通过状态转移来改变 Context 所组合的 State 对象,而策略模式是通过 Context 本身的决策来改变组合的 Strategy 对象。
-
-所谓的状态转移,是指 Context 在运行过程中由于一些条件发生改变而使得 State 对象发生改变,注意必须要是在运行过程中。
+状态模式的类图和策略模式类似,并且都是能够动态改变对象的行为。但是状态模式是通过状态转移来改变 Context 所组合的 State 对象,而策略模式是通过 Context 本身的决策来改变组合的 Strategy 对象。所谓的状态转移,是指 Context 在运行过程中由于一些条件发生改变而使得 State 对象发生改变,注意必须要是在运行过程中。
状态模式主要是用来解决状态转移的问题,当状态发生转移了,那么 Context 对象就会改变它的行为;而策略模式主要是用来封装一组可以互相替代的算法族,并且可以根据需要动态地去替换 Context 使用的算法。
@@ -1969,7 +1965,7 @@ public abstract class CaffeineBeverage {
```
```java
-public class Coffee extends CaffeineBeverage{
+public class Coffee extends CaffeineBeverage {
@Override
void brew() {
System.out.println("Coffee.brew");
@@ -1983,7 +1979,7 @@ public class Coffee extends CaffeineBeverage{
```
```java
-public class Tea extends CaffeineBeverage{
+public class Tea extends CaffeineBeverage {
@Override
void brew() {
System.out.println("Tea.brew");
@@ -2238,7 +2234,7 @@ Number of items: 6
### 意图
-使用什么都不做的空对象来替代 NULL。
+使用什么都不做的空对象来代替 NULL。
一个方法返回 NULL,意味着方法的调用端需要去检查返回值是否是 NULL,这么做会导致非常多的冗余的检查代码。并且如果某一个调用端忘记了做这个检查返回值,而直接使用返回的对象,那么就有可能抛出空指针异常。
@@ -2393,7 +2389,7 @@ public abstract class TV {
```
```java
-public class Sony extends TV{
+public class Sony extends TV {
@Override
public void on() {
System.out.println("Sony.on()");
@@ -2412,7 +2408,7 @@ public class Sony extends TV{
```
```java
-public class RCA extends TV{
+public class RCA extends TV {
@Override
public void on() {
System.out.println("RCA.on()");
@@ -2551,9 +2547,6 @@ public abstract class Component {
```
```java
-import java.util.ArrayList;
-import java.util.List;
-
public class Composite extends Component {
private List child;
@@ -2659,7 +2652,7 @@ Composite:root
### 类图
-装饰者(Decorator)和具体组件(ConcreteComponent)都继承自组件(Component),具体组件的方法实现不需要依赖于其它对象,而装饰者组合了一个组件,这样它可以装饰其它装饰者或者具体组件。所谓装饰,就是把这个装饰者套在被装饰上,从而动态扩展被装饰者的功能。装饰者的方法有一部分是自己的,这属于它的功能,然后调用被装饰者的方法实现,从而也保留了被装饰者的功能。可以看到,具体组件应当是装饰层次的最低层,因为只有具体组件的方法实现不需要依赖于其它对象。
+装饰者(Decorator)和具体组件(ConcreteComponent)都继承自组件(Component),具体组件的方法实现不需要依赖于其它对象,而装饰者组合了一个组件,这样它可以装饰其它装饰者或者具体组件。所谓装饰,就是把这个装饰者套在被装饰者之上,从而动态扩展被装饰者的功能。装饰者的方法有一部分是自己的,这属于它的功能,然后调用被装饰者的方法实现,从而也保留了被装饰者的功能。可以看到,具体组件应当是装饰层次的最低层,因为只有具体组件的方法实现不需要依赖于其它对象。
@@ -2770,7 +2763,7 @@ public class Client {
### 实现
-观看电影需要操作很多电器,使用外观模式可以实现一键看电影功能。
+观看电影需要操作很多电器,使用外观模式实现一键看电影功能。
```java
public class SubSystem {
@@ -2811,7 +2804,7 @@ public class Client {
### 设计原则
-最少知识原则:只和你的密友谈话。也就是客户对象所需要交互的对象应当尽可能少。
+最少知识原则:只和你的密友谈话。也就是说客户对象所需要交互的对象应当尽可能少。
## 6. 享元(Flyweight)
@@ -2822,8 +2815,8 @@ public class Client {
### 类图
- Flyweight:享元对象
-- IntrinsicState:内部状态,相同的项元对象共享
-- ExtrinsicState:外部状态
+- IntrinsicState:内部状态,享元对象共享内部状态
+- ExtrinsicState:外部状态,每个享元对象的外部状态不同
@@ -2854,8 +2847,6 @@ public class ConcreteFlyweight implements Flyweight {
```
```java
-import java.util.HashMap;
-
public class FlyweightFactory {
private HashMap flyweights = new HashMap<>();





















